Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
IMAGE: Deployment of an APEX float from a German research ship.
Credit: Argo
The global ocean represents the most important component of the Earth climate system. The oceans accumulate heat energy and transport heat from the tropics to higher latitudes, responding very slowly to changes in the atmosphere. Digital gridded climatologies of the global ocean provide helpful background information for many oceanographic, geochemical and biological applications. Because both the global ocean and the observational basis are changing, periodic updates of ocean climatologies are needed, which is in line with the World Meteorological Organization’s recommendations to provide decadal updates of atmospheric climatologies.
“Constructing ocean climatologies consists of several steps, including data quality control, adjustments for instrumental biases, and filling the data gaps by means of a suitable interpolation method”, says Professor Viktor Gouretski of the University of Hamburg and a scholarship holder of the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ President’s International Fellowship Initiative (PIFI) at the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the author of a report recently published in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters.
“Sea water is essentially a two-component system, with a nonlinear dependency of density on temperature and salinity, with the mixing in the ocean interior taking place predominantly along isopycnal surfaces. Therefore, interpolation of oceanic parameters should be performed on isopycnals rather than on isobaric levels, to minimize production of artificial water masses. The differences between these two methods of data interpolation are most pronounced in the high-gradient regions like the Gulf Stream, Kuroshio, and Antarctic Circumpolar Current,” continues Professor Gouretski.
In his recent report, Professor Gouretski presents a new World Ocean Circulation Experiment/ARGO Global Hydrographic Climatology (WAGHC), with temperature and salinity averaged on local isopycnal surfaces. Based on high-quality ship-board data and temperature and salinity profiles from ARGO floats, the new climatology has a monthly resolution and is available on a 1/4° latitude-longitude grid.
“We have compared the WAGHC climatology with NOAA’s WOA13 gridded climatology. These climatologies represent alternative digital products, but the WAGHC has benefited from the addition of new ARGO float data and hydrographic data from the North Polar regions”, says Professor Gourteski. “The two climatologies characterize mean ocean states that are 25 years apart, and the zonally averaged section of the WAGHC-minus-WOA13 temperature difference clearly shows the ocean warming signal, with a mean temperature increase of 0.05°C for the upper 1500-m layer since 1984”.
###

“available on a 1/4° latitude-longitude grid” Is that one quarter of a degree, in other words 15nm of latitude?
And the increase in rate of sea level is where?
And the decrease in the earth’s rotational rate?
How much CO2 out gassing would that create?
Argo data from 1984? What did I misread there?
Bah. Splice two disparate records and you can make up anything you like.
Call it the “Chinese Academy of Sciences Ocean Temperature Nature Trick” (h/t Tony Heller).
If anyone reading this doesn’t get the reference, here’s background:
https://sealevel.info/climategate.html
The ARGO float data is completely useless for measuring ocean temperature over time. They float freely so you cannot measure temperature changes in a specific location over time. Gridding the data is worse than a bad joke; it’s statistical malfeasance. The only thing they are good for is measuring temperature changes with depth, but only brief snapshots over a single measurement period. Any study purporting to show ocean warming from ARGO float data is a farce.
stinkerp, I think that you misunderstand how the ARGO deep diving buoys actually work. From their parking (drift) depth of about 1000m below the surface, about once every 10 days they first descend to 1500-2000 m depth then begin measuring an ascending profile of temperature, salinity, etc. This profile is obtained over a typical ascent duration of about 6 hours. Once the buoy reaches the surface it radio transmits the just-completed profile measurements as well as its GPS position, typically through the Iridium satellite system. Having completed this data communication, the buoy then descends again to its parking (drift) depth to repeat the cycle. ARGO floats vary slightly in design and mission due to continuing hardware and software improvements.
Given the range of lateral velocities of typical ocean currents and that such currents are in relative narrow ranges of depth , it is doubtful that during the 6 hours ascent duration the location of the measurement profile would be spread over more than the 0.25 deg latitude x 0.25 deg longitude grid spacing discussed in the above article (equivalent to 69 statute miles by 60 sm @equator/49 sm@45-deg latitude).
Thus, it is fair to say that ARGO diving buoys (not “floats”) are indeed useful for measuring quite localized (0.25 deg x 0.25 deg) ocean temperatures/profiles for each ascent they make, which itself ends with GPS-accurate positioning.
Ummm…Gordon, I already knew that, which is why I wrote what I did. The buoys float freely in the ocean which means that temperature data over days, weeks, and months are for different areas of the ocean. There is no temporal precision beyond a single measurement dive (6 hours) or two. Useful for measuring the temperature profile at a single random location, but completely unusable for measuring temperature changes over time because of the drift.
And they are indeed “floats” not “buoys”. Look it up yourself:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Argo_(oceanography)
http://www.argo.ucsd.edu/
A buoy is anchored to the ocean floor. The ARGO floats are not anchored. They drift freely with the current.
Ooops . . . at the end of my second paragraph above, the statute mile distances are for a full degree of lat & long (I forgot to divide by 4). The corrected sentence should read ” . . . would be spread over more than the 0.25 deg latitude x 0.25 deg longitude grid spacing discussed in the above article (equivalent to 17 statute miles by 15 sm @equator/12 sm@45-deg latitude).
I stand by my conclusion given the following additional information:
“On either side of the equator, in all ocean basins, there are two west flowing currents: the North and South Equatorial. These currents flow between 3 and 6 kilometers per day and usually extend 100 to 200 meters in depth below the ocean surface. . . . Flowing from the equator to high latitudes are the western boundary currents. These warm water currents have specific names associated with their location: North Atlantic – Gulf Stream; North Pacific – Kuroshio; South Atlantic – Brazil; South Pacific – East Australia; and Indian Ocean – Agulhas. All of these currents are generally narrow, jet like flows that travel at speeds between 40 and 120 kilometers per day. Western boundary currents are the deepest ocean surface flows, usually extending 1000 meters below the ocean surface. . . . Flowing from high latitudes to the equator are the eastern boundary currents. These cold water currents also have specific names associated with their location: North Atlantic – Canary; North Pacific – California; South Atlantic – Benguela; South Pacific – Peru; and Indian Ocean – West Australia. All of these currents are generally broad, shallow moving flows that travel at speeds between 3 and 7 kilometers per day. . . . The world’s oceans also have significant currents that flow beneath the surface. Subsurface currents generally travel at a much slower speed when compared to surface flows.” — source: http://www.physicalgeography.net/fundamentals/8q.html
One needs to carefully note the quote of Professor Gourteski given in the very last sentence of the above article:
“The two climatologies characterize mean ocean states that are 25 years apart, and the zonally averaged section of the WAGHC-minus-WOA13 temperature difference clearly shows the ocean warming signal, with a mean temperature increase of 0.05°C for the upper 1500-m layer since 1984”.
1) The World Ocean Atlas 13/World Ocean Database 13 database did not exist in 1984; an earlier version must have been used (e.g., WOA05/WOD05, WOA09/WOD09, whatever).
2) There was no ARGO data gathering system, or anything comparable, in the years (decades) leading up to 1984, so clearly subtracting a “1984” dataset from the WAGHC dataset (which includes the ARGO data measurements) is mixing apples with oranges.
3) What is the procedure for either “zonally averaging” each section of each database prior to “subtraction”, or alternatively, for “subtracting” the earlier data from the more recent data for each zone prior to “averaging” the data across the zone?
4) Most interestingly, why did this study only look at the 25 year time span from 1984 (i.e., not consider data from 2009 until the last year or two)? Is there something in the last 10 years of data, particular that coming from the extensive ARGO precision measuring network that might result in a contrary or inconclusive finding? (And please, don’t claim that it took about 10 years to get this report published!) Is this a classic case of cherry picking the data to obtain an end result?
As it stands right now, the above issues and questions lead me to assert the above-referenced report is so much GIGO.
Like the nice auditor that spent four days at our facility this week, I would like to see the calibration results for these thermometers. What was the scheduled calibration frequency, was it adequate, what was the as found condition, etc.? So many variables to control in a decent lab to claim that kind of accuracy, so much harsher conditions 1500 meters below the surface of the ocean. I’m not from Missouri, but show me.
Why was the ARGO project built in the first place? Because we couldn’t measure ocean temperature well until then. Prior to ARGO, ocean temps were measured not deep enough and concentrated in areas important to anti-submarine warfare.
ARGO is like trying to sample the heights of people randomly sampled around the world from different countries, ages, sexes. Suppose I try comparing those data with a 1984 study that quantified the heights of people in military boot camps. It is a silly comparison. It is possible to do the arithmetic, but it is either a STUPID exercise, or a MISLEADING exercise.
Just so with this study to compare ARGO with a non-ARGO study. Their claim of 1984 destroyed any credibility they ever had. Or will have. How could any self-respecting scientist put their name to such drivel?
It is amazing what people will do and/or claim to have done, in order to get their grant money signed over.
Anyone fancy a trip down to the Galapagos islands to test the water temperature? There is a research grant with your name on, to do that.
Uhuh… because ARGO works correctly (it doesn’t).
The entirety of ocean temperature data collection prior to ARGO was a sloppy 3°C error fest and even with ARGO its still a sloppy 2°C error fest.
0.05C
No wonder all the coral, fish, prawns, whales, kelp etc are dying faster than evah
“Constructing ocean climatologies consists of several steps, including data quality control, adjustments for instrumental biases, and filling the data gaps by means of a suitable interpolation method…”
So not real measurements again then! And they only managed to find 0.05C – that must be the ‘climate science’ wooden spoon winner right there!
Here is an idea. Do some limited research up to say 1984, then graft on some other data from a more modern data source to ensure the end result looks like a…… well a flat hockey stick.
Then to ensure the research gets full coverage in the world wide press, get the BBC preferably using David Attenborough, to declare the ocean’s temperature is increasing at an astonishing rate. Make a natural world documentary, showing Chinese street sellers stir frying fish, then tell the wider public, the Ocean temperature has risen by 500 degrees C in just 35 years! The fact most watching won’t know the difference between 5 hundredth of a degree and 5 hundred degrees is just detail.
After all what is a “th” between friends in the global warming community.
Have to wonder if their choice of 1984 was a Freudian Slip or possibly even a conscious subtle clue that they knew that this paper is little more than Orwellian Doublespeak thinly disguised with a dose of statistical and data splice masturbation.
Meanwhile, while reading this post my body temp went from 37C to 37.05C and my BP went up from 120/60 to 120.05/60.05. Yikes! running a fever and hypertensive both! Must be from the CO2 I inhaled when I opened that last beer. Better get to the ER fast or I won’t be around to watch the world end in 12 years!
Nice catch. I missed the connection.
Maybe they should carry out a real scientific research project.
1. Look for ocean areas that are warming more than the average.
2. Look for a reason.
JF
I agree. I think Guoretski is working out a kind of baseline that can be useful. And he is one of the most serious scientists.
And I get tired of all the comments at WUWT that meet every scientific finding by spitting it out. You need no intelligence to do that. There is no willingness to learn, and understand. The real interesting question is how energy is distributed. And this is about ocean currents.
It takes intelligence and honesty and common sense to be a serious scientist – none of those are evident in this type of work.
Nobodysknowledge, your last sentence is probably the most pertinent. Possibly the most valuable information at the moment (I nearly wrote ‘currently’) from ARGO is increasing knowledge of ocean currents and oscillations and their mechanisms. Gordon Dressler has listed some of those known above, there must be many more we are as yet unaware of and some of them will operate far below the depths of ARGO.
The absolute temperature measurements are of interest, but will not be of great value until their statistical validity is improved by greatly increased sampling. Also, is it more relevant to measure the temperatures within a moving column of water (ARGO) or would there be more value in measurements at a fixed geographic point?
Calibration, sensor aging and the effects of pressure on measuring instruments are variables which are not taken into great account and has been said many times already in these comments, Guoretski ‘s work, as you say, a foundation for others to build on, is devalued by concatenation. Without reference to his original work I will not comment on the lack of error bars, but five hundredths degree K in a third of a century seems neither significant nor relevant to current discussions.
Gouretski uses a decimal point to show he has a sense of humor.
Just so we are clear about this shattering study.
The top 1500 metres of the oceans which are roughly 3700 metres deep, is all of 0.05deg C warmer than it was 35 years ago.
Call me Mr Underwhelmed, but are we supposed to
a) take this 0.05 figure as real or just best guess?
b) be in any way concerned about it?
It’s worse than you think. I don’t feel like looking it up, but each argo float represents about 45,000 square miles. The simple fact is: WE DON’T KNOW WHAT THE OCEAN’S TEMPERATURE IS.
Each argo float floats in the water it is in. It doesn’t measure a new area; it measures the same water it measured 10 days before, just in a new location.
Someone needs to explain how CO2 and LWIR between 13 and 18µ can possibly warm the oceans. The warming of the oceans is the greatest evidence that CO2 isn’t causing the warming. What warms the oceans warms the atmosphere, and it ain’t CO2.
Why the Sun Controls the Climate and CO2 is Meaningless
https://co2islife.wordpress.com/2018/06/09/why-the-sun-controls-the-climate-and-co2-is-meaningless/
CO2isLife asked, “Someone needs to explain how CO2 and LWIR between 13 and 18µ can possibly warm the oceans.”
When water (or anything else) absorbs radiation of any wavelength (including 13 -18 µm radiation), it warms.
When air warms, for any reason, it warms anything in contact with that air (or, if the thing in contact with the air was already warmer than the air, the air cools it more slowly).
Any other questions?
Doesn’t 0.05 C since 1984 over the top 1500 m equate to a bit less than 0.20 W/m2 average over the Earth’s surface? Or about 100 ZJ in total? That is rather less than other datasets indicate, I think.
Nic Lewis wrote, “Doesn’t 0.05 C since 1984 over the top 1500 m equate to a bit less than 0.20 W/m2 average over the Earth’s surface? Or about 100 ZJ in total?”
Well, let’s see…
The oceans cover about 3.618 × 10^8 km² (sq-km) = 3.618 × 10^14 m² = 3.618E14 m².
So the volume of the top 1500 m of the ocean is about:
1500 m × 3.618 × 10E14 m² = 5.427E17 m³ = 5.427E20 liters.
It takes 1000 cal to raise one liter of water by 1 °C.
So, to raise 1 liter of water by 0.05 °C requires 1000 × 0.05 = 50 cal.
So, to raise 5.427E20 liters of water by 0.05 °C requires 50 × 5.427E20 = 271.35E20 cal = 2.7135E22 cal.
1 cal = 4.184 J, so 2.7135E22 cal. = 11.3533E22 J = 1.13533E23 J.
1 ZJ = 1E21 J, so 1.13533E23 J = 1.13533E22 ZJ = 113.533 ZJ.
It’s been pointed out that their “since 1984” apparently only ran through 2009 (why?!?), so it’s 25 years, rather than 34 or 35.
1 W = 1 J/sec.
25 years = 25 × 265.25 × 24 × 60 × 60 = 572940000 sec = 5.7294E8 sec.
So, 1.13533E23 J / 5.7294E8 sec = 1.9816E14 W.
1.9816E14 W / 3.618E14 m² = 0.5477 W/m².
(If you’d used 35 years instead of 24, it would work out to 25/35 of that = 0.3912 W/m².)
CORRECTION:
I typo’d a couple of the numbers, starting with the number of days in a year. The last four lines should be:
25 years = 25 × 365.25 × 24 × 60 × 60 = 788940000 sec = 7.8894E8 sec.
So, 1.13533E23 J / 7.8894E8 sec = 1.4391E14 W.
1.4391E14 W / 3.618E14 m² = 0.3978 W/m².
(If you’d used 35 years instead of 25, it would work out to 25/35 of that = 0.2841 W/m².)
Even if this study is accurate – which it almost certainly isn’t – it doesn’t matter as it still does not explain what warmed the oceans as CO2 simply can not do it.
The downwelling argument does not address where the energy magically came from nor does it explain how something that can only penetrate the oceans by ±10µm) which would by the IPCC’s own typically optimistic calculations warm the oceans by only 0.002°C for a doubling of atmospheric CO2. This is literally too insignificant to measure and certainly too little to be discerned against the background noisiness of the data.
The oceans are heated by the Sun and practically nothing else.
Further the oceans give up that heat to the atmosphere via the hydrological cycle / latent heat of evaporation etc.
Air temperature is colder over the oceans (generally) than the air above – as Flanders and Swan once sung “you can’t move heat from a cooler to a hotter, you can try it if you like but you far better notta”. (The Thermodynamics Song).
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mw-brvKO-Z
For the atmosphere to (generally) heat the oceans violates the second law of thermodynamics and the problems of boundary effects prohibit warm air from heating the oceans in any case (try heating a bowl of water using a hot air gun against the surface only and see how far it gets you).
The temperature of the atmosphere drives the phenomena of “Weather” out to about 2-3 weeks but longer term weather, atmospheric temperatures and thence “Climate” is driven by ocean temperature hence the desperation of the alarmists to prove that something patently impossible within the accepted laws of physics is driving Climate Change.
They need to prove CO2 is heating the oceans !
CO2 does not and can not warm the oceans – Solar variance and the Milankovic cycles do – but man is not responsible for those.
Any argument that clashes with the second law of thermodynamics is doomed.
Ergo: man made climate change via the miniscule thermodynamics of CO2 is impossible – QED
Ken Irwin wrote, “The downwelling argument does not address where the energy magically came from nor does it explain how something that can only penetrate the oceans by ±10µm) … you can’t move heat from a cooler to a hotter … For the atmosphere to (generally) heat the oceans violates the second law of thermodynamics … CO2 does not and can not warm the oceans … [etc.]”
I am so, so, so tired of this “sky-dragon slayer” nonsense. ☹️
Please, everyone, just stay away from those anti-scientific “Principia-Scientific International” nutters, unless you like being lied to and confused.
Ken wrote, “(try heating a bowl of water using a hot air gun against the surface only and see how far it gets you).”
Why don’t you try it, Ken? Measure out two bowls of water, as nearly identical as you can manage. Put two identical thermometers in them, and verify that they show the same temperature. Then hit one of them with a hot air gun for a few minutes. Then measure the water temperatures again.
Or, if you don’t have a heat gun, you could a similar experiment at lower temperatures: Measure out two bowls of warm water (warmer than room temperature). Put one of them in the refrigerator overnight, and leave the other one on the kitchen counter. Check their temperatures in the morning.
Notice how much warmer the bowl left on the counter is, even though the air temperature in the room was cooler than the water temperature. The air in your kitchen kept the water warmer, even though the kitchen ambient air temperature was cooler than the water temperature — and the 2nd Law was not violated.
Ken Irwin wrote, “…how something that can only penetrate the oceans by ±10µm)…”
If you want to understand how the top 10µm of a body of water can absorb 15 µm LWIR radiation without losing that absorbed energy to evaporation, see this comment on Steve Carson’s blog.
Dave, point taken – your suggested “cooler” experiment does not violate the second law but does not address the problem as I postulated it.
The atmosphere over the oceans is generally cooler than the oceans and is heated by the oceans via evaporation / condensation delivering the latent heat to the atmosphere etc.
For the (generally) cooler atmosphere to heat the oceans requires the violation of the second law.
The hot air gun is hyperbole – but it is ineffective – try it with a hair dryer on cool (still a greater differential than you will find on Earth for the small area that is subjected to offshore warmer winds) and between boundary and evaporative cooling effects you will find your experiment confounded.
“Soundbite” science either way, entire explanations are lengthy, tedious, incomplete and contentious.
Ken Irwin wrote, “For the (generally) cooler atmosphere to heat the oceans requires the violation of the second law.”
Wrong. That’s the “sky dragon slayer” fallacy.
If you were right, then it would mean coats are a scam. There would be no point wearing a coat in freezing weather, because a coat is always cooler than 98.6°F (37°C), so it could not possibly warm your body, since that would violate the 2nd law of thermodynamics.
That sort of confusion is why you should not read the garbage that PSI disseminates. (I assume that IS where you read it, right?)
It is such pure, refined nonsense that it inspired me to wax poetic. With apologies to the late, great Ogden Nash, I give you:
Sky Dragons
The Second Law they twist and shove,
to slay their dragons from up above.
But this I know by actual test:
Use a blanket and you’ll shiver less.
The title (“Sky Dragons”) is from the name of a truly awful book entitled, “Slaying the Sky-Dragon.” Avoid it, unless you like being lied to and confused.
As I understand it, even if DWIR did purely drive evaporation (which it doesn’t) it wouldn’t change the fact that this can still be part of the oceans accumulating heat content. The amount of evaporation that can happen is constrained by Clausius-Clapeyron (humidity / saturation vapor pressure etc.) and therefore the energy used to drive evaporation is energy that (on average across the global ocean) would have otherwise have been ‘taken’ from the water (warmer water naturally evaporating more). Less evaporative cooling of the water with consistent solar heating means the water warms. In that framing the DWIR is more like an insulating role (insulation warms your room by slowing heat loss from it, not by heating it directly). But there is a lot of IR…
This type or reanalysis is really just “scientific” self stimulation. It allows that if the “researchers” have an underlying agenda (to find warming whether real or not) they need only continuously play with measurement tools, numbers, statistical tests, models of data etc. month after month and ignore every result but the one which shows their deepest desire – then publish that. If that is what they have done then it is not science but advertising for a product (global warming catastrophe) which they are selling at a high profit to themselves. As for the discovery of methods for measurement that may have more accuracy I have no argument – if they are used reliably and consistently to measure into the future rather than to try and reanalyze the past.
BTW, the heat content of the oceans is known, the change in heat content is known, the W/M^2 of IR back radiation from CO2 is known, the BTUs associated with that back radiation is known, it is very easy to calculate that even if 100% of the CO2 back radiation is absorbed by the oceans, there is no way to warm the oceans that much. The warming of the oceans is clearly due to fewer clouds and a cleaner stratosphere allowing more blue visible radiation to reach the oceans.
El Ninos are driven by warming due to visible radiation, and when they release all that energy into the atmosphere and roll over into a La Nina, the temperature change in the oceans would take CO2 decades to replace all the lost energy. Only visible radiation significantly warms the oceans.
” there is no way to warm the oceans that much.”
Why is it so difficult to understand??
They are NOT being warmed.
They are NOT being allowed to COOL as efficiently.
“They are NOT being allowed to COOL as efficiently.”
That is absolute nonsense.
1) El Nino’s do the cooling in a very very rapid manner. At best, CO2 could slightly decrease the time between El Ninos
2) H20 saturates the LWIR between 13 and 18µ above the oceans, so with or without CO2 the back radiation is identical. You can check this with MODTRAN and put the settings to looking up into the lower 0.1 km of the atmosphere.
CO2isLife wrote, “H20 saturates the LWIR between 13 and 18µ above the oceans, so with or without CO2 the back radiation is identical.”
That’s incorrect. Here’s the Earth’s measured LW IR emission spectrum, looking down from a satellite over the tropical western Pacific:
The effect of water vapor’s absorption is circled in blue.
The effect of CO2’s absorption is (appropriately) circled in green.
As you can see, there is a fair amount of overlap on the long-wavelength side of CO2’s absorption band. But H2O doesn’t absorb much on the short side of CO2’s absorption band.
It is true that additional atmospheric CO2 has only a small & logarithmically diminishing warming effect, but it’s not mainly because of the water vapor. It’s mainly because there’s already so much CO2 in the atmosphere. MODTRAN tropical atmosphere calculates that just 0.002% CO2 (by volume or molar fraction) would have fully half the warming effect of the current 0.04%.
“That’s incorrect. Here’s the Earth’s measured LW IR emission spectrum, looking down from a satellite over the tropical western Pacific:”
Once again, pure nonsense. This effect is modeled in MODTRAN. What is relevant to the oceans is the back radiation immediately above the oceans, not the stratosphere. LWIR in the stratosphere isn’t warming the oceans. That air is so thin there in no energy being trapped anyway. Astronauts would freeze to death in the “hot” thermosphere. Place a bag of water in the “hot” thermosphere and it will freeze. Total amount of energy is what warms the oceans, not some IR temperature measurement.
Chart #9 and 10: The other problem with ground measurements is that water vapor saturates the Greenhouse Gas Effect of the lower atmosphere. The CO2 “signature” isn’t even measurable until you are at an altitude of 3.5km or above. 100% of all ground measurements are taken in the layer of the atmosphere where CO2 has absolutely zero impact. By relying on the “adjusted” ground measurements, Climate Alarmists are allowed to claim warming, and attribute it to CO2. In reality, the only warming in the lower atmosphere is due to greater sunlight reaching the earth’s surface and oceans, water vapor, the Urban Heat Island Effect and intentionally biased data “adjustments”, not CO2.
https://co2islife.wordpress.com/2018/08/11/comprehensive-climate-change-debating-points-and-graphics-bring-it-social-media-giants-this-is-your-opportunity-to-do-society-some-real-good/
” LWIR in the stratosphere isn’t warming the oceans.” Absolutely correct!….not only that, LWIR from anywhere in the atmosphere isn’t warming anything.
…
LWIR from the atmosphere is retarding cooling, it doesn’t “warm.”
…
Just like a winter jacket in cold weather!!!
P.S. — in that image, of the Earth’s LWIR emission spectrum over the tropical western Pacific, you’ll see a trace marked “thunderstorm anvil,” which approximately follows the 210 K blackbody curve.
Here’s a nice page about “thunderstorm anvils,” with some very nice photos of of them:
https://fox41blogs.typepad.com/wdrb_weather/2012/07/crazy-clouds-the-thunderstorm-anvil.html
Thunderstorm anvils are composed of ice crystals, and they form at the tropopause, which is the boundary between the troposphere and stratosphere, where the “lapse rate” drops to zero. Temperatures there are around 210 Kelvin (-63.15°C = -81.67°F), the coldest altitude in either the troposphere or stratosphere.
The fact that CO2’s “green notch” in the Earth’s emission spectrum, centered on 15 µm, dips right down to the same weak intensity that you’d expect from a 210 K blackbody (same as the thunderstorm anvil temperature) tells us that at the center of CO2’s 15 µm absorption band the average “emission height” is right at the tropopause.
Higher CO2 levels raise that 15 µm emission height, but (contrary to erroneous information found on many sites, including both RealClimate and SkepticalScience) that wouldn’t decrease emissions of 15 µm radiation, because the lapse rate is approximately zero at that altitude. So the warming effect from additional CO2 is mainly from the fringes of that green notch, at wavelengths where the emission height is lower, because CO2 only weakly absorbs & emits at those wavelengths.
RealClimate (here) and SkepticalScience (here), both get that wrong. But not all the climate alarmists are confused about it. Ken Rice gets it right on his ATTP blog.
“It is true that additional atmospheric CO2 has only a small & logarithmically diminishing warming effect, but it’s not mainly because of the water vapor. It’s mainly because there’s already so much CO2 in the atmosphere. ”
That is absolutely pure nonsense.
CO2 is 400 ppm, and its marginal addition to W/M^2 of anthropogenic CO2 is measured in very very low single digits. A simple cloudy day can wipe out months of back radiation from CO2. The marginal absorption of energy by CO2 shows a rapid logarithmic decay, so doubling CO2 will barely alter the energy balance.
The problem the Climate Alarmist’s scam faces is that the W/M^2 absorbed by CO2 isn’t linear like the CO2 trend, it shows a logarithmic DECAY. Unlike the “Hockey Stick” that shows linear warming with the linear CO2 increase, the marginal W/M^2 actually DECREASES with additional CO2. From the following chart, CO2 added 29.8 W/M^2 to the atmospheric energy budget when it increased from 0.00 ppm to the pre-industrial 300 ppm maximum level. The post-industrial CO2 increase from 300 to 400 ppm added an additional 1.38 W/M^2, and doubling CO2 from 400 ppm to 800 ppm will add an additional 3.33 W/M^2. To put those numbers in perspective, a simple cumulus cloud layer can “trap” 28.7 W/M^2 without any catastrophic consequences to warming.
https://co2islife.wordpress.com/2019/03/02/hockeystick-con-job-co2-cant-cause-temperature-dog-legs/
0.05° in water on global scale is a lot of energy. That point seems lost on many readers.
As for instrument accuracy, some types of statistical noise will simply cancel out with mass readings. As such accuracy can indeed go up from a single reading. There are different problems with the black art of averaging and potential bias in methods but the potential to read numbers to this degree of accuracy appears as factual.
John:
1. Statistics (i.e. the theory of large numbers) don’t work with independent measurement devices measuring independent things. It only works with one measurement device taking multiple readings of one thing.
2. Accuracy and resolution are two different things. Being able to “read” a measurement to a specific number of significant digits doesn’t mean that measurement is accurate.
CO2 Can’t Cause Catastrophic Warming as Long as El Niño, La Niña and Hurricanes Exist
Water has the highest specific heat of any other common material at 1 calorie/gram °C = 4.186 joule/gram °C (Source), and therein lies the problem, CO2 and Long-Wave Infrared Radiation between 13 to 18µ doesn’t provide a lot of energy to warm the oceans. Visible radiation, the radiation that penetrates and warms the oceans, very high energy radiation between 0.4 to 0.7µ bathes the oceans with about 1050W/m^2 on a sunny summer day at noon. (Source) Anthropogenic CO2, the difference between 270 and 410 ppm provides a marginal 0.94W/m^2 24×7. (Source) CO2’s contribution is literally like adding a garden hose to the Alaskan Pipeline.
Rita and Katrina cooled some parts of the oceans by a full 4°C. One m^3 of water contains 1,000,000 grams. CO2 can warm 1 gm of water every 4.45 seconds (4.186/0.94). To warm one m^3 of water 1°C would take 4,450,000 seconds or 75,000 minutes, or 1,250 hours, or 7.44 weeks or 1.86 months…and this assumes Long-Wave Infrared Radiation between 13 to 18µ actually warms the oceans. To replace the full 4°C of energy lost would take over 7 months…JUST TO GET BACK TO EVEN!!!
https://co2islife.wordpress.com/2019/01/19/co2-cant-cause-catastrophic-warming-as-long-as-el-nino-la-nina-as-well-and-hurricanes-exist/
“and this assumes Long-Wave Infrared Radiation between 13 to 18µ actually warms the oceans.”
Only those who do not the science “assumes LWIR …. warms the oceans”.
Just as on land it, is an ‘insulating’ effect.
Because back-radiated LWIR is increasing, the oceans are cooling to space less effectively.
Solar SW warms the oceans, and back-radiated LWIR slows cooling to space.
“Solar SW warms the oceans, and back-radiated LWIR slows cooling to space.”
Unless MODTRAN is wrong, CO2 has absolutely 0.00% impact on the energy balance in the atmosphere below 3km. The only time the CO2 signature is even measurable is when the H2O precipitates out and the atmospheric temperature drops to around the blackbody temp of 15µ. At that altitude, the thinness of the air alllows for radiation to COOL the atmosphere, not slow its warming. Radiation out moves much faster than conduction or convection. You can show no warming of the stratosphere with an increase of CO2, nor can you show a “hotspot” in the upper troposphere. It makes absolutely 0.00 sense to claim that the oceans can absorb 15µ, but water vapor doesn’t. MODTRAN also shows that H2O does effectively absorb 100% of 15µ
“MODTRAN also shows that H2O does effectively absorb 100% of 15µ”
No it does not, as H2O does not fully mask CO2 around that wavelength….
And here shows HITRAN doesn’t “effectively absorb 100% of 15 micron” …
https://static-content.springer.com/esm/art%3A10.1007%2Fs00704-016-1732-y/MediaObjects/704_2016_1732_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
As a sup material to …
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00704-016-1732-y
HITRAN shows also that there is a strong absorption line at 4 micron that H2O barely touches.
Good info, Anthony B.
However, the 4 µm absorption band doesn’t matter much. At 4 µm the Earth emits little radiation, so there’s little or no so-called “greenhouse effect” from the 4 µm absorption.
A rule of thumb is that the cutoff wavelength, below which (longer than which) the Earth emits more than it receives, is about 4 µm. Google finds lots of graphs:

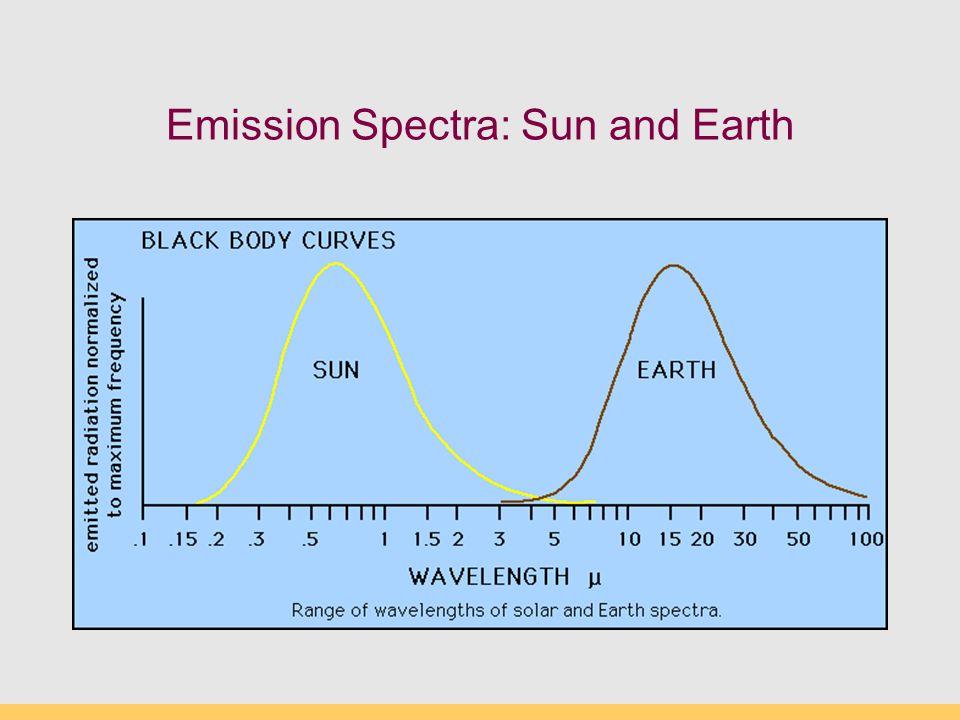
https://www.google.com/search?q=earth+and+sun+emission+spectra&tbm=isch
E.g.:
The so-called (misnamed!) “greenhouse effect” only works with wavelengths longer than about 4 µm.
Anthony, that spectrum is most likely from a gas cell of about 10cm long. You are 100% correct, H2O does not absorb 100% in a 10cm distance. Take it up to 2 m or the height of a Stevenson Screen and you will see H2O absorbs 100%. You can verify that at Spectral Calc. They have a gas cell calculator there.
“Take it up to 2 m or the height of a Stevenson Screen and you will see H2O absorbs 100%. absorbs 100%.”
islife: Yes, when there is any of significance there.
The GHE works primarily where is is little WV- aloft, over deserts and the poles (except it works in reverse – at least some of the time – in Antarctica).
I refer you to:
https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/wea.2072
“Table 1 presents the contributions of the individual gases (derived from the areas
under the curves in Figure 4(b)). The second row in the table shows the impact of the
individual gases on downward radiation incident at the surface. This component is
dominated by H2O due to the very strong emission of radiation by the near-surface
atmosphere through the H2O continuum described above. At the top of the atmosphere,
however, the continuum has little effect as most of the radiation emitted by H2O in lower layers has been absorbed and the emergent radiation has been emitted
from layers at lower temperatures. For CO2, on the other hand, some of the radiation
from the surface manages to reach space. Thus the net effects of H2O and CO2 at
the top of the atmosphere are much more similar than at the surface and it can be seen
that, despite having a concentration of less than 0.04%, CO2 is responsible for nearly a
quarter of the total greenhouse trapping of radiation in the current atmosphere under
clear-sky conditions.”
“The CO2 15μm band occurs close to the peak of the blackbody function at temperatures
representative of the Earth’s atmosphere and surface. It also happens to occur where
water vapour absorption is weaker and thus it plays a key role in infrared radiative transfer in Earth’s atmosphere. “
CO2isLife wrote, “Take it up to 2 m or the height of a Stevenson Screen and you will see H2O absorbs 100%.”
I don’t think so, CO2isLife. The measurements which go into the HITRAN database are, indeed, lab measurements. But the graph that Anthony showed is the result of a calculating the effect of those measurements on the entire atmosphere.
Anthony B’s graph is consistent with the satellite-measured emission spectrum: substantial H2O absorption on the long-wavelength side of CO2’s absorption band, but only weak H2O absorption on the short-wavelength side of CO2’s absorption band, as you can see:
Pray tell, where does one find such?