Guest Post by Willis Eschenbach
I got to thinking about the classical way to measure the very poorly-named “greenhouse effect”, which has nothing to do with greenhouses. To my knowledge, this method of measuring the greenhouse effect was first proposed by Raval and Ramanathan in a 1989 paper yclept “Observational determination of the greenhouse effect“.
Their method, followed up to the present by most everyone including me, is to subtract the upwelling (space-bound) longwave (LW) radiation measured by satellites at the top of the atmosphere (TOA), from the upwelling surface longwave radiation. Or as they describe it in the paper, which was only about the ocean:
” We obtain G by subtracting longwave radiation escaping to space from estimates of the radiation emitted by the ocean surface.”
This measurement is said to represent the amount of upwelling surface radiation absorbed by the atmosphere. This can be expressed either as watts per square meter, or as a percentage or a fraction of the surface emission.
Figure 1 shows this measurement of the all-sky “greenhouse effect” around the world. It shows the amount of energy absorbed by the atmosphere expressed as a fraction of the underlying surface emission.

Figure 1. Atmospheric upwelling longwave (LW) absorption as a fraction of surface longwave emission.

Figure 1a. As in Figure 1. Changes over time of atmospheric longwave (LW) absorption as a fraction of surface longwave emission.
So … what’s not to like?
Today, while pondering a totally different question, I realized that the Ramanathan measurement, while not useless, is also not accurate. There are two issues I see with the measurement.
Other Energy Inputs To The Atmosphere
About 40 W/m2 of upwelling surface longwave goes directly to space. The rest of the ~240 W/m2 of upwelling LW comes from the atmosphere, not the surface.
The first issue with the Ramanathan method is that the atmosphere only gets about two-thirds of its energy flux from absorbed upwelling surface longwave radiation. The other third of its energy flux comes from two totally different sources— 1) solar energy absorbed by the atmosphere, aerosols, and clouds, and 2) latent (evaporative) and sensible (conductive) heat loss from the surface to the atmosphere.
As a result of these other energy fluxes entering and leaving the atmosphere, changes in the top-of-atmosphere (TOA) longwave measured by satellites using the Ramanathan method may merely reflect changes in solar absorption or changes in latent/sensible heat loss. Here’s the total of the other energy going into the atmosphere.

Figure 2. The sum of two other sources of energy fluxes absorbed by the atmosphere.
As you can see, these other sources of atmospheric energy flux vary over time. Part of this additional energy flux is radiated to space, messing with the Ramanathan estimate of the greenhouse effect.
Up Versus Down
The second issue is that the atmosphere radiates in two directions, up and down. However, the ratio between upwelling and downwelling longwave (LW) radiation is not constant. Here is the variation in TOA upwelling longwave due solely to the changing upwelling/downwelling ratio.

Figure 3. Variations in top-of-atmosphere longwave (TOA LW) radiation due solely to the variations in the ratio of atmospheric energy going upwards and downwards.
The variations in these two other energy fluxes, variations that will appear in the amount of energy heading out to space, will cause spurious variations in the Ramanathan greenhouse measurement.
A Better Metric??
Seems like if we considered the TOA LW as a fraction of the total energy entering the atmosphere, rather than as a fraction of upwelling surface LW, it might be more instructive … hang on, never done this … well, dang, this is interesting.

Figure 4. As in Fig. 1a, except comparing the upwelling TOA longwave radiation going to space to total atmospheric energy flux, rather than comparing it just to upwelling surface longwave.
Hmmm … not sure what to say about that. It does seem that the fraction of atmospheric energy flux going out to space hasn’t changed much over the 22-year period of record. And it certainly has not increased by the amount we would expect from the increase in CO2 forcing …
All ideas welcome.
My best wishes to all,
w.
The Usual: Please quote the exact words you are discussing. It avoids a host of misunderstandings.
The system is kept stable because the thermal effect of any increase in radiative gases is neutralised by changes in convection.
Those changes being far too small to discern compared to natural variability.
That nets out a very complex interaction. Mother nature rules.
And the Earth doesn’t have a roof.
Yes, and convection is not inhibited by atmospheric CO2, but greenhouses work by preventing convection of heat. Therefore the “Greenhouse Effect” is a complete misnomer.
They came up with that phony name to in order to scare people, for the idea of being trapped in a greenhouse on a hot day is terrifying.
I don’t think they planned this. They wrote their atmospheric models – which they wanted to believe as their careers depended on the status as “expert” modellers. Then it seems they bullied and gaslit everyone into accepting the notion that empirical science was impossible as there is ONLY ONE PLANET EARTH, and the precious greenhouse gas effect needed the whole planet as an experiment, which we could not risk. We had to apply a precautionary principle and believe the models written by “experts”. LOL. Despite the fact their GHG model is a 1-dimensional joke model. Over time they cancelled their critics, so ended up in an echo-chamber. The echo chamber amplifies their group think.
I know the whole thing looks like psychopathology or fraud, but it’s really just careerism spun out of control.
Disagree. It is not “just” any one thing.
I think there are many reasons. Many climate apocalysts believe in the myth of peak oil, the myth of limited resources, the myth of overpopulation… and the myth of the sixth great extinction. All of these myths are interchangeable in the mind of many climate apocalysts. They may think “if oil/resources is going to run out, or there are too many people, we need to curb that, but how? I know, lets tell a white lie about the climate”. I think it is driven more by politics and narcissism than anything. Its also politically expedient to have some scapegoat to avoid responsibility, or responsible policy, or to put on the facade of a hero of the environment for political points.
I would think, if they wanted to scare people, they would have named it the “hothouse effect”. Greenhouse just isn’t scary.
“I would think, if they wanted to scare people, they would have named it the “hothouse effect”. Greenhouse just isn’t scary.”
Absolutely. I don’t think they choose that name to be scary. They choose it because they were ignorant.
How appropriate that their cherished theory’s name is based on ignorance and junk science!
Chris
“They” didn’t come up with that name – it was Dalton, in the 1860’s, wasn’t it?
Hansen’s model says this greenhouse gas effect is happening at the top of the troposphere. But reality says convection dominates cooling at pressures of about 3 Torr and above; which is the lower stratosphere. But even at the lower stratosphere conduction then takes over. I don’t think radiation dominates the cooling until the mesophere is reached.
Warmists bullied everone into accepting their models. They have no science. They’ve never measured a greenhouse effect at the surface. We’ve all been gaslit.
Just to be clear are the top of the atmosphere measurements taken at the top of the troposphere?
TOA measurements are not actually taken inside the atmosphere at all – they are made by satellites orbiting outside the atmosphere using instruments that remotely register the radiation. Obviously, if satellites were obiting inside the atmosphere they wouldn’t last very long.
The edge of the atmosphere is subjective
If climate “science” is a real science- not being a scientist, I’d think that that science would definitively define the edge to make it objective.
The atmosphere has no edge.
The gas molecule concentration just gets gradually more tenuous.
There is nothing analogous to a surface or edge.
No place where parameters undergo a sudden shift.
As such, any edge would be 100% arbitrary.
And it is not constant.
In periods of high solar activity, the upper atmosphere heats up and expands, and when solar activity is low, it cools and contracts.
Ad this variance is not negligible or inconsequential.
In the 1970s, we lost our first space station, called Skylab, when solar activity ramped up more and faster than expected or predicted, slowing the satellite and causing it to de-orbit and crash to Earth in an uncontrolled crash landing.
It could have been really bad, instead of merely costly.
There was a plan to boost the orbit to a higher level before it was in danger, but the Sun had other plans, and we did not have the capacity to move up the schedule as needed.
Not really. For practical purposes it is an altitude of 100km, where atmospheric blue fades to black as imaged by ISS. CERES instruments fly on several satellites, with orbital altitudes from ~400 to ~800 km.
Sounds pretty subjective .. “For practical purposes“
That’s life. The “top of the atmosphere” will shift according to how hot the air is, from the heat of the Sun plus time of day/year plus any space weather weirdness.
It’s enough for this purpose that the satellite is above the top of the atmosphere, to measure the energy emitted.
The top will also shift based on the gravity of the moon
Atmosphere tides, no different than the ocean
The absolute definition would be “where no matter can be retained by the gravitational attraction of the body in question.”
But that is not at all useful in practical terms. At the very edge of this definition, you would count perhaps one molecule in several cubic kilometers. It also shifts and changes shape constantly, as the other two commenters noted.
There are many different edges. The ISS has to be reboosted from time to time because it is slowed down by atmospheric drag, even at its altitude. There are those who say that aerodynamic drag can occur up to 700 km altitude.
If the TOA measurements are made by a nadir-viewing satellite, then it misses both the diffuse-scattered rays, and the specular reflections outside the viewing cone of the satellite sensor. One can estimate the un-measured diffuse reflections from a BRDF model. One can also correct for the specular reflections for high angles of incidence; however, I don’t think anyone is doing that.
Actually, they use a space-borne detector tuned to a specific IR band. Basically, they are seeing how brightly lit the Infrared bulb called Terra glows.
I content that the brightness of a light source tells you little as to its exact emission power. They answer me by telling me they’ve calibrated their measurements against known presumptions…
But did they calibrate against known assumptions? The word “presumption” seems like a weasel word compared to “assumption”- since it is an assumption with a presumption of knowing the fact(s).
| I conten[d] that the brightness of a light source tells you little as to
| its exact emission power.
You are correct, in the sense that the energy E of a photon of IR light is determined by its frequency ν, E=hν
So the power spectrum of Earth’s outgoing radiation is a function of ν and its absolute temperature T (in K) and peaks in the IR spectrum around 12.5 microns wavelength, according to Planck’s Law of Radiation.
So we can call this IR (longwave) radiation, emanating from Earth, “earthshine”.
The top of the atmosphere is defined at 100 km (60 km in some studies). Satellites orbit the Earth at different altitudes, but typically 600 km. They are still inside the atmosphere (exosphere) and are subject to atmospheric drag that limits their useful life.
100 km is a legal convention incorporated into treaties. As a legal construct, it probably has very little to do with science or facts.
Doesn’t CO2, and other greenhouse gases, also absorb the longwave radiation from the Sun and send part back towards space cooling the atmosphere?
Yes, radiation is radiation, absorbent gases select the wavelength, not the source.
But I understood the whole hypothesis presumes a positive feedback from increased water vapor…about as difficult to measure as average global temperature.
So many unknowns in supposed “settled science”.
I should think, as a non scientist speculating, that whether or not there is a positive feedback from increased water vapor should easily be resolved in a physics lab. Perhaps there is sometimes under some conditions and not under other conditions. Seems to me that “climate science” is still in its infancy. Too many variables with very dynamic energy flows to get a grip on.
Unlike CO2 which is fairly evenly mixed in the atmosphere and very precisely measured, water vapor, the most powerful greenhouse gas, is widely variable in the atmosphere, in both geographic location and time.
Not measurable.
NASA/RSS measures it. Maps at RSS / Microwave Climate Data Record (CDR) / Browse Imagery (remss.com)
anomalies at https://data.remss.com/vapor/monthly_1deg/tpw_v07r02_198801_202212.time_series.txt
Sure, a snapshot geographically and temporally, but constantly changing.
Next el Nino, el Nina, in between? What are historical TPW measurements, and what will they be in the future? Remember, H2O is the#1 greenhouse gas, this is not trivial.
Minute 8:29
“big difference… is due to something called the h20 continuum. Well you ask what is the h2O continuum due to and no one seems to know” William van Wijngaarden
https://youtu.be/KaUmDZEAhbE?si=4yWTHFVgODbFe_3y
Thanks for that link, worth reading for everybody because it is short, credible and fantastic to fire off at ones “ settle science “ neophyte friends.
I do not disagree, but that would also mean a temperature of the Earth is NOT MEASURABLE.
Correct: “temperature of the Earth is NOT MEASURABLE.”
From Wiilis’ post: “other sources of atmospheric energy flux vary over time.”
The same with Temperature, Total Precipitable Water Vapor, upwelling surface LW… You name it, climate is always changing over all time scales. Any fixed value attached to it is a comforting abstraction, but not reality.
I don’t agree with this.
Planets radiate to the cosmic background at some temperature. As Johanus pointed out, this temperature is related to peak wavelength of radiative emissions through Planck’s Law of Radiation. Shifts in the temperature related in this way to peak wavelength implies global cooling or heating (assuming constant solar input) by simple consideration of the Earth’s energy budget.
Interesting work is currently being conducted in this manner to determine characteristic temperatures of exoplanets.
To claim that temperatures calculated in this way for Mars, Earth, Venus, exoplanets, etc have no logical meaning is wrong. The effective radiative temperature is crucial to the Earth’s energy budget. These elaborate parsing schemes to determine if there is or isn’t global warming are superfluous to the measurement of peak wavelength emissions and then radiative temperature to the cosmic background that determines crucial outflow for the Earth’s cosmic energy budget.
I accept your point.
However, does it not seem likely that at some point the earth will enter another ice age, thus radiate at a lower temperature?
This is my point, that climate varies on all time scales, and the real climate change damage is being done by silly efforts to avert it.
Agreed. Earth’s climate was changing before human’s appeared and will continue to change in the event humans become extinct.
Thank you for the reply.
Even without looking for a visible presence of water vapour in the atmosphere, a barometer provides a guide to how it changes in the column of air above that location, at times almost, for those with the time, whilst the barometer is being watched. Those with a home weather station will have an ongoing daily recording of it to refer to.
This is why the climate models have real problems – then can’t handle clouds correctly, which is also water vapor. It’s also one reason why UAH can’t accurately measure true temperature. UAH measures radiation from the atmosphere, but that radiation gets modulated by cloud cover which UAH can’t measure. So the variance of the data from UAH is pretty high but not measurable, meaning its u measurement uncertainty is also high. As usual with climate science, the uncertainty quoted for UAH is really the SEM, i.e. how precisely they can calculate the average of the data – but that doesn’t tell you much about the accuracy of the average you have calculated. Baseline? Don’t depend on UAH measuring temperature changes in the hundredths digit. It’s no different than the GAT when it comes to measurement uncertainty.
I wonder what the uncertainty of the CERES data is.
water vapor is a transparent gas, clouds are condensed liquid water droplets or ice particles.
Water vapour is tricky. It rises forming clouds which reflect back sunlight (cooling) then sneaky blighter condenses, falls as precipitation releasing its latent heat of vaporisation to Space (cooling).
You just cannot trust it to do what climatrons want.
The take away is that “climate science” is just now taking its baby steps yet we hear every day that “the science says…”.
We don’t need no steenkin’ physics lab: The absence of a Tropospheric Hot Spot disproves CliSciFi’s constant-relative-humidity-driven-water-vapor-positive-feedbacks-tripling-CO2-warming as programmed into UN IPCC CliSciFi climate models.
But, but, but… we should burn hydrogen because it produces no carbon dioxide just water vapour, er….?
Only a small part of the sun’s output is in the bands absorbed by CO2.
Yes. But there is significantly more outgoing terrestrial radiation in the band 13-15 um than there is incoming solar radiation at the same frequency. A quick back-of-the-napkin calculation shows 13 W/m2.sr for outgoing terrestrial and only 0.05 W/m2.sr for incoming solar.
I have no idea why you get 5 thumbs down for this comment. You are correct to within the uncertainty of some of this. I calculate that the entire IR band from 4um to as long a wavelength as one can imagine represents only about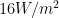 of solar radiation. All of this must be IR because it is longer than 4 um. I get around
of solar radiation. All of this must be IR because it is longer than 4 um. I get around  for that little slice between 13 and 15 um. This is using the Blackbody functions available in most heat transfer textbooks.
for that little slice between 13 and 15 um. This is using the Blackbody functions available in most heat transfer textbooks.
But I get about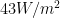 for the LWIR input from a blackbody at the ground surface upward into the sky 13-15 um if one assumes 288K.
for the LWIR input from a blackbody at the ground surface upward into the sky 13-15 um if one assumes 288K.
And then you’ve got the higher energy absorbed from the (more variable) solar UV.
It was always my understanding that this stratospheric warming of the atmosphere is what effectively sets the level of the tropopause. It is the lid on the weather that goes on underneath.
That in itself seems like a good justification for some complex computer climate models, but I’m still not convinced they are getting right.
Interesting year, 2014; 79 volcanic eruptions occurred, lots of stormy weather and, according to the temperature-obsessed statisticians, ‘the hottest year since 1880.’
Make of that what you will, with reference to the graphs Willis has kindly posted, of course.
“The hottest year since 1880” isn’t very impressive figuring that the Earth is in a 2.5 million-year ice age and 20 percent of the land is either permafrost or covered by glaciers.
I agree, I was merely mentioning what climate enthusiasts came up with.
climate fantasy enthusiasts
1880? heck, I think one my grandfather’s was born that year- not that long ago- practically zero on a geologic time scale
“20 percent of the land”…..and 72% of earth is water?…..hmmmmm, maybe that’s why I feel crowded?…only 8% for living.
Twenty percent of the total land. Not 20 plus 72.
20 % of the 28% that is not water , so that leaevs you with 80% of the 28% or roughly 18% of the total surface.
“It does seem that the fraction of atmospheric energy flux going out to space hasn’t changed much over the 22-year period of record.”
IIt seems that the stability of this ratio can’t just be written off as a coincidence and must have an explanation grounded in first principles. If preferred a ratio exists, it would have no dimensional constraints leaving mathematical self consistency as a dominant constraint.
Check to see if this ratio is the same in both hemispheres.
In Raval & Ramanathan it is defined G = E – F where E is upwelling longwave from the surface and F is upwelling longwave from top-of-atmosphere.
It looks like you have defined it as G = (I + L + S) – F where I is incoming shortwave radiation absorbed by the atmosphere, L is latent absorbed by the atmosphere, and S is sensible absorbed by the atmosphere. Is that correct?
Or is it G = ((E – W) + I + L + S) – F where W is the atmospheric window at around 40 W/m2?
bdgwx September 28, 2023 10:45 am
Yes.
And regarding the atmospheric window, I’ve left that out because this is a first cut. You could subtract 40 W/m2 from the data if you wish for a rough calculation. If you wanted more detail you’d likely want to modify it for temperature because it’s likely a percentage of total surface upwelling LW.
w.
Trenberth did a great disservice to climate science by putting non radiant heat into the energy balance while inferring that it’s also relevant to the radiant balance, which is all that matters relative to the sensitivity of the surface temperature to changes in the radiant input to the system (the only real forcing). The S-B emissions at the average surface temperature is explicitly a part of his balance and already accounts for the full influence of non radiant energy entering the atmosphere plus its offset back to the surface, which he then accounts for a second time inferring that they have additional effects beyond those they already have. Furthermore, if a Joule of LW that leaves TOA can trace its origin to latent heat, a Joule of surface S-B emissions that would have left TOA must be returned to the surface to offset the lost latent heat.
An even more constant ratio will be observed by removing non radiant heat entering the atmosphere and considering the ratio of the LW radiation exiting TOA and the Stefan-Boltzmann emissions of the surface. You’ve already shown, using this same data source, that the long term average of this ratio is statistically the same dimensionless constant in both hemispheres. You should also be able to show that this ratio doesn’t vary much from year to year, globally or per hemisphere. That this ratio is so immutable is what drives other long term ratios to be relatively constant. Another relatively constant ratio is the yearly average fraction of the surface covered by clouds which happens to be a different constant
per hemisphere. Another is the yearly average fraction of the S-B surface emissions absorbed by clouds and GHG’s, which is about the same per hemisphere.
First, Trenberth didn’t put non-radiant heat into the energy balance. That was [Dines 1917] who did that via the L term in his diagram. L captures both sensible and latent flux.
Second, Trenberth (or anyone) who develops an energy balance must include all fluxes of energy otherwise it would be a violation of the 1st law of thermodynamics.
No that’s not right. Latent and sensible fluxes are different modes of transmission. They are not included in the upwelling longwave flux.
That’s the canonical GHE. G = E – F where E is the radiant exitance at the surface and F is the radiant exitance at the TOA.
@bdgwx
Dines WH. The heat balance of the atmosphere. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society. 1917 Apr;43(182):151-8.
That is a stunningly good reference.
I missed that one.
The Library – Climate Audit 101
From Dines 1917
This comment quite something:
My point is that there’s a difference between the energy balance and the radiant energy balance and relative to the effect of GHG’s, only the radiant balance has any relevance. The reason is that only radiant energy can enter and leave the planet while including non radiant energy to the mix adds unnecessary wiggle room for speculation. For example, the nominal sensitivity speculated by the IPCC infers that an incremental W/m^2 of forcing will result in about 4.4 W/m^2 of incremental surface radiation (0.8C), while the radiant balance tells us in undeniable terms that each W/m^2 of net solar forcing, including the next one, will uniformly result in only about 1.6 W/m^2 of surface emissions (about 0.3C). No Joule, independent of its origin, can do more work than any other (the unit of work is the Joule) and replacing radiant emissions to maintain an average temperature is quantifiable work. It’s common knowledge that Watts are rate of Joules, right?
“No that’s not right.”
https://scied.ucar.edu/image/radiation-budget-diagram-earth-atmosphere
Look at the 396 W/m^2 of ‘surface radiation’. This is the SB radiation at his somewhat exaggerated average surface temperature of 289K that he explicitly includes and since the average surface temperature already accounts for the effect of latent heat and thermals plus their offset to the surface, why add them again except to obfuscate?
Latent heat is also the largest source of the Joules driving weather and those Joules are not returned as ‘radiation’ as is inferred, but most is returned as the work of weather and of course from the phase change of water vapor back into a liquid (i.e. rain) at a temperature that’s warmer than it would be otherwise. Lumping this in as ‘downwelling radiation’ is another obfuscation that serves only to make the system seem more radiantly complex than it actually is.
“That’s the canonical GHE.”
E-F also includes surface radiation absorbed by the liquid and solid water in clouds which is not narrow band GHG absorption, but is the broad band absorption of more total energy than all GHG’s combined. Also bear in mind that incremental GHG’s between the surface and clouds are irrelevant to incremental atmospheric absorption, as the clouds would absorb that surface energy anyway.
Is that capturing the GHE and only the GHE though?
Two issues.
1. The up welling ir intercepted by co2 is saturated. See the recent Happer paper. Going from the current 400 ppm to 800 ppm is negligible. The Happer paper was discussed on this site recently.
2. The discussion of downwelling Ir from co2 has always been nothing but spin based on radiative equilibrium of which convection blows apart part of it and the actual mechanism that co2 radiates with is ignored. In short, I want to see a plot from the surface to the top of troposphere that plots the percentage of co2 in their quantum excited state. Their is a disconnect in general between the macro(thermalization of co2 states) de-excitation/excitation and quantum theory. The non-lte analysis they use in the stratosphere could deal with this but I have found no one trying to extend it to the earth’s surface.
3. Happer gives the individual power radiation for co2 excited states(along with spontaneous/induced time constants). The co2 time constant is heavily weighted to the spontaneous side. But providing a plot of the percentage of co2 excited states over the troposphere is not there.
4. The claim that the co2 emmisivity is settled is absolutely not supported.
5. The modtran downwelling estimates for co2 in my opinion are not realistic. I want the to see a co2 excitation plot over the the lower atmosphere to the troposphere.
6. If Climate models are using the co2 downwelling predicted similar to the modtran estimates, they should be believed when it comes to co2 sensitivity.
Can anybody tell where to find this plot. This plot along with the co2 ir path length will determine ir downwelling from co2. With out this plot….. ???
DT, If you want someone to read “the Happer paper”, provide a link.
In friendship,
w.
Posted above
https://wattsupwiththat.com/2021/09/21/the-greenhouse-effect-a-summary-of-wijngaarden-and-happer/
Here is link to summary of paper. Will try to find link to actual paper.
Probably this is the droid you’re looking…
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.16465.pdf
That is correct latest one.There is also an earlier version 2018 or so.
Thanks, have papers but lost links.
Not correct. More CO2 in the atmosphere means more CO2 in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere where it is not saturated and has an effect. In fact, you can keep adding CO2 all the way to having an atmosphere like that of Venus.
By what mechanism does more CO2 in the stratosphere raise the planet’s temperature?
More CO2 absorbs more IR radiating from the surface…warmer CO2 bumps the surrounding 2500 air molecules and makes them a bit warmer. Then, cuz the air is a bit warmer, the next day the sun can warm the surface a bit more….and so on it goes. Not that difficult. And not much warming either but nevertheless…
Not correct. A number of things contribute to the atmosphere and temperature of Venus. Among them is the fact that its atmosphere is far denser than Earth’s, and it is a lot closer to the Sun.
More importantly, the surface of Venus in direct equilibrium with solar energy is high up in the cloud tops where the surface temperature below is dictated by the PVT profile of a compressed gas starting from the temperature of the cloud tops giving it’s lapse rate the opposite sign of Earth’s. In principle, its atmosphere is equivalent to our ocean, relative to heat storage, mass, density and its isolation from direct solar energy.
That’s not quite right. Venus’s lapse rate it very similar to Earth’s. ok, about double…see fig 11 below.
Venus is hot at surface because it has 90 times as much atmosphere as Earth, and a 11 degree lapse rate for 50 Km down from its mean radiative temperature to the surface, wheras Earth only has about 5.5 km from mean radiative altitude to surface, and a lapse rate of about 6 degrees/km so Earth only gains about 33 degrees (versus Venus’s 550 degrees hotter). I have not followed the convention of lapse rates being negative, colder with increasing altitude here, sorry…
Lapse rate is primarily a result of convecting parcels of warm atmosphere cooling as they rise to lower pressure at higher altitude by buoyancy (and vice versa for falling parcels). You can blame it on Venus’s CO2 causing a huge greenhouse effect if you wish, but really that high surface temp of Venus is the result of convective lapse rate and a really thick atmosphere.
Wanna make Mars warmer…give it a thicker atmosphere somehow….
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1806.06835.pdf
You’d have to add a HECK of a lot of CO2 to our atmosphere to get “one like Venus.” ~90 bar at the surface, there.
Some years back, I took a look at the Venusian temperature profile derived from the various landers. Now, that data is quite coarse, as they spent little time in the various layers, plus the composition is obviously different – but the temperature measured where the pressure is ~1 bar (Earth sea level) IS higher. Most of that difference, however, is easily explained by factoring in the calculation for received solar energy at the orbit of Venus. Only about five degrees Celsius does not disappear, even with this very rough calculation.
DT in regard your number 4.
Not even close to being in correct realm. This is extrapolated furnace data.
Atmosphere is mixture of gas. N2/o2/co2 80/20 percent/ 400ppm
Much lower overall pressure and temp.
Completely different dynamics….
6.0 should not be belived…
Been a while since I posted here, what happened to edit button
I’ve come to the conclusion that almost all the major energy transfers is through the oceans. Atmosphere is very short life span. The energy being absorbed in the tropics and distributed by ocean currents. It explains the long deep march to the cold world we live in today. Today the world expresses almost all the energy through storms and such as evaporation becomes a major way energy gets transported through the atmosphere and then down, making deserts where they are. This energy is very short term, measure in weeks, goes away within 2 months.
Oceans have become cold because the energy doesn’t get transferred around like it often did descending after increasing salinity and warming the bottom of the ocean and then gets pushed up that happens during warm times. The energy gets expressed almost all in the tropics, and the cold waters outperforms the warm waters going do to the bottom of the ocean and we have oceans averaging 5 degrees. The plate tectonics restricts waters movements and few inland seas that can warm the oceans and expressing through the atmosphere and increased cloud cover.
My 2 cents. Atmospheric GHG is a minor determinate of climate, where continents are and how that plays with how energy gets expressed is the biggest determinate in the cold climate of today.
If you want we can go into how interglacials happen through cycles, storage, and currents in the ocean.
Becomes a discussion of what can be controlled if everyone else were to comply with the controller’s will.
hmmmmm- that’s actually a rather profound metaphysical comment…. the sort of idea that Robert Lawrence Kuhn discusses in his YouTube podcast
”We obtain G by subtracting longwave radiation escaping to space from estimates of the radiation emitted by the ocean surface.”
I can’t access the paper, but this would be a very important detail. I assume they have an emissivity of water of 1, or very close to it. In reality the emissivity of water is only 0.91. We know this not just because of my work and so the fact itself is hard to dispute. Still “climate science” ignores it basically. At 288K for instance emissions then are not 390W/m2, but only 355W/m2.
How could you fix this, from a consensus perspective? G. Schmidt on Twitter:
I fail to see why you think there is some big conspiracy here? Tables for emissivity etc get updated all the time without having much impact on sensitivity or overall estimates of the GHE. You have, however, neglected LW reflection in your description of upward LW.
Yep, just add the LW radiation reflected by the surface. Then of course it is no more radiation emitted the surface, but surface upwelling radiation (emitted or reflected).
However it actually will NOT fix the problem. If there were no GH-constituents, there would neither be any LW radiation to be reflected by the surface. As we are asking, or at least by the definition of Ramathan above, how much GH-constituents reduce emissions, surface emissions IS the right term.
E. Schaffer September 28, 2023 11:30 am
Nah. Actually, it’s very close to 1.
https://scienceofdoom.com/2010/12/27/emissivity-of-the-ocean/
From that comprehensive analysis:
Best to you,
w.
FYI
https://greenhousedefect.com/what-is-the-surface-emissivity-of-earth
I smell a Total Stinking Rat – from the figures provided by Sputnik – this thing is entirely fixed as the figures are Just Too Good.
By reference to Figure 3 and the numbers on the vertical axis – let’s say 243W/sqm
Run that past Stefan to get -17.1°C
Then add in the ‘magic’ 33°C uplift from GreenHouseGases to get a (slightly high) figure of 15.86°C for Global Average temperature.
Sorry no – It’s just too damn good to be true
That’s kind of a screwed up thought process, Peta. The -17C is what you get using Stephan Boltzmann and an Albedo of .3 for the planet. Earth’s Albedo is mostly due to its 65% cloud cover, sorta between Venus, all clouds A=.75 and the Moon, cloudless A=.13
Then the 33 C is due to the lapse rate from the altitude where the atmosphere is -17…down to the surface at an average lapse rate of about 6.4 C per km. Thus the 33 C is mostly due to convective properties of the atmosphere and much less to do with GHG, although GHG obviously must affect Lapse rate to some extent….
The atmospheric energy gradient has been shown to be absolutely linear wrt molecular density… always meeting the gas laws PV=nRT
Thermodynamic equilibrium… rules !
That would seem to indicate that the gas laws are controlling the combine total energy transfer.
FYI equations 44 and 61 for temp gradient , dry adiabatic.
https://www.tec-science.com/mechanics/gases-and-liquids/barometric-formula-for-an-adiabatic-atmosphere/
It always amazes me when warmists can’t answer why CO2 is not a variable in lapse rate since CO2 has a direct affect on temperature.
Our profs always reminded us that the Ideal Gas Law only applies to ideal gases.
An ideal gas has two obvious properties: the individual gas particles are infinitesimally small, and there are no inter-molecular forces. Real gases fail on both points. However, real gases behave more like ideal gases when the pressure is very, very low, and the temperature is very, very high.
“Thermodynamic equilibrium… rules !”
That’s true, but I don’t understand your point. The atmosphere has never been in equilibrium since its inception. Therefore, it doesn’t have a Thermodynamic temperature.
The diagram shows continents as position references but air moves so the references might give a funny impression. Like why more lingwave in the jungle than the desert?
Also scoring a point for the opponent- using charts that don’t start at zero because we care about variations not totals.
This is not at all surprising. The 500 millibar height is the same as the effective radiating height of the atmosphere. About 5.5 km average. This cannot be coincidence.
The lapse rate is about 6C/km which gives 33C of warming at the surface as compared to the -18C at 5.5km.
The energy gained below 5.5 km is the energy lost above 5.5km.
This cannot be moved by CO2 because it is governed by mass and rotation.
A simple question at the end.
Preamble: The temperature of -18C is the average temperature of the earth as calculated without GHG. This is the observed average temperature of the earth at the Effective Radiation Height. A height of approximately 5.5 km. When multiplied by an approximate lapse rate of 6 c/km this gives the theoretical 33 C of GHG warming.
However, the 5.5 Km height is also the approximate height of the 500 millibar height. The half mass of the atmosphere.
Now there is some good argument to leave out the atmosphere above the troposphere, which might serve to improve the fit, but leave this aside for now.
Question: why should the Effective Radiating Height coincide so closely with the 500 millibar height? Does this explain why GHG theory is wrong?
As the former head of the UNIPCC stated- the environmental movement is more about the destruction of capitalism – so all the technology and science is merely to support the overall goal of installing a totalitarian worldwide government
Figure 4 is closer to the surface and lower troposphere temperature changes, very slight cooling 2002-2014 then warming post 2014.
What frequency bands do the ocean surfaces emit LW at? could it be mostly within the atmospheric window?
Is your Issue 1 just another way of describing the ‘forgotten feedback’ that Lord Monckton is so enthused about?
WE, nice analysis. Not sure it leads to any likely conclusions since you are working from CERES, so start in 2000.
My problem is we know of at least three NH natural cycles that require longer time frames to attempt to separate natural from AGW (and it’s not clear whether your expected CO2 red lines are total effect including feedbacks, or just CO2 without feedbacks. The former observational ECS is about 1.7C, the latter is (per Lindzen) about 1.2C):
One possible work around would be to just use the SH half of CERES, as I know of no established natural cycles for those oceans. Might be worth a try, as you have the R programming already set up.
Assuming the surface latent and sensible heat is derived from CERES surface net radiation, or the surface Net Total Flux parameter, or Net SW + Net LW, it’s fraught with uncertainties so it’s kinda forced to fit. Particularly the downwelling longwave portion with dependence on radiative transfer codes relying on estimates of column water vapor and surface air temperature, causing 5 + 5 Wm-2 uncertainty respectively at minimum just in the downwelling LW (~10 Wm-2). neat approach tho. Surface net radiation isn’t really known to better than sum total 20 Wm-2 exhibited by the bizarre changes in the IR window flux of that magnitude in various energy balance schematics. It’s not a small problem.
Are there any numbers for the CERES irradiance uncertainties?
Calibration uncertainty on raw radiances is thought to be about 1% or equivalent to about 2 Wm-2. Conversion to flux is empirical and introduces more uncertainty. Loeb optimistically reports all-sky TOA flux unknowable to better than about 3 Wm-2 at 1-sigma. As usual for this type of thing there is no available validation and so judgement creeps in. https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/clim/31/2/jcli-d-17-0208.1.xml
Thanks, will take a look at this paper.
the important bit to realize is that the reported data values at TOA are effectively forced to match changes in ocean heat content. CERES EBAF data are not an independent measure, they are constrained. For the actual measurement envelope draw bare minimum 3 Wm-2 bars on the LW and SW components. It’s inconvenient.
Numbers of this magnitude should not be a surprise because they are typical for radiometric measurements — a global pyranometer on the surface will usually be 4-5%, or 0.5 W/m2 at 1000 W/m2. With a lot of attention to the details it is possible to get better than this, but not a lot better. And as you pointed out subtracting or adding two CERES quantities increases the uncertainty. Regarding infrared pyrgeometers needed for the Trenberth diagrams, I’ve not seen a formal analysis, but I can’t believe they could be any better than pyranometers. Just on the basis of the much smaller signal levels I would have to guesstimate them as 10% instruments.
At each and every subtraction or addition step in the Trenberth diagrams, the uncertainty grows.
thank you. Yes, the “energy balanced” constrained CERES EBAF v4.* products are set simply to match alleged temperature equivalent change of 0.4 Wm-2/decade irrespective of observational uncertainties.
CERES all-sky LW~ -0.3 Wm-2 decade-1
CERES all-sky SW~ +0.7 Wm-2 decade-1
The unavoidable conclusion when taking CERES EBAF products at face value is that surface and atmospheric emission of LW is over-compensating the effective longwave radiative forcing of 0.35 Wm-2 decade-1. i.e. no net enhancement of atmospheric heat trapping blanket stuff.
Net accumulation of energy can only be associated with albedo effects during the CERES period, and of that overwhelmingly cloud albedo effects.
Heh, means nothing in the long run and this comment is late, but I went to high school and college with one of the authors of this paper. Smart, good friend, never discussed climate change with him.
BTW…speaking of CERES…the net TOA flux is now +1.48 W/m2 and +1.97 W/m2 averaged over 36m and 12m respectively. For point of comparison the radiative force of CO2 alone is only about 5.35 * ln(420/280) = 2.2 W/m2 assuming [Myhre 1998] is correct. It is looking more and more like we may have underestimated aerosol forcing, GHG forcing, shortwave feedback, or a combination of them.
Or it’s something else entirely and you’ve been barking up the wrong tree this whole time?
Willis,
Your metric may be interesting, but is it measuring the greenhouse effect? That is normally understood to be the extra warming at the surface produced by GHGs. Ramanathan captured that by subtracting TOA LW from surface LW, which is related to surface T.
But you have replaced surface LW by fluxes elsewhere. There isn’t anything about the surface any more.
Nick, you imply a very narrow GHE definition. Most warmunists are not so narrow. For example, all their feared extreme weather effects arise in the troposphere, only to then affect the surface. For example, all the CMIP6 models address the full troposphere. All but one of CMIP6 say the GHE produces a tropical troposphere hotspot. The sole exception, INM CM5, has an ECS of 1.8, close to observational EBM estimates ~1.7.
But a lot of what you talk about there is not the GHE. The tropical hotspot (which does exist) is the result of any kind of warming, evaporating more water at the surface.
“The tropical hotspot (which does NOT exist) “
If you hold the paper sideways, use a black light and squint, you to can see what ever you want to see.
Nick writes
Actually additional evaporation resulting in a hotter hotspot is the result of more energy, not “warming”.
Its a subtle but important difference IMO, particularly when you consider the amount of energy required to increase the energy in the hotspot is not particularly tightly related to changes in a minimum and/or maximum recorded daily temperature.
Clarification (for any “newcomers” or “lurkers” wondering what the heck Nick is going on about).
The “tropical hotspot” refers to a feature of many climate models which show enhanced rates of warming in the troposphere, normally shown as a “red-hot” oval from roughly 30°N-30°S latitudes and from 150-300 hPa pressures (/ “altitudes”).
The IPCC’s AR6 (WG-I) assessment report touched on this subject in section 3.3.1.2.1, “Tropospheric temperature”, on pages 443 to 445 :
A copy of Figure 3.10 is included here for enlightenment (hopefully) :
Notes (on “panel a”)
– RICH (radiosonde data analysis) doesn’t show any change in warming trends up to 300 hPa
– RAOBCORE (ditto) has a very small and shallow “peak” from 400 to 300 hPa, but nothing to get excited about
– the ERA5 reanalysis product has a roughly linear increase in trends from the surface up to a peak at 150 hPa
– the “coupled ocean” climate models have “enhanced warming rates” from 300 to 150 hPa, with a peak at 200 hPa … a “profile” that neither the “raw” radiosonde datasets nor the ERA5 reanalysis exhibit …
_ _ _ _ _
Post Scriptum …
Just because you are the person claiming to have managed to, for example, “deconvolve” the complex issues around the tropospheric hotspot isn’t “proof” that your assertions are true.
Yes, I know that is not your intention, but that is how you are coming across !
The last time the IPCC included a “visually obvious” graphic of the hotspot was back in AR4 (2007), in Figure 9.1 of the WG-I report.
The caption is copied (from page 675) below.
“Figure 9.1. Zonal mean atmospheric temperature change from 1890 to 1999 (°C per century) as simulated by the PCM model from (a) solar forcing, (b) volcanoes, (c) well-mixed greenhouse gases, (d) tropospheric and stratospheric ozone changes, (e) direct sulphate aerosol forcing and (f) the sum of all forcings. Plot is from 1,000 hPa to 10 hPa (shown on left scale) and from 0 km to 30 km (shown on right). See Appendix 9.C for additional information. Based on Santer et al. (2003a).“
I made a brief video a while back explaining the tropical hotspot and why it does not disprove GHG-driven global warming:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J4kTdsfaZ2g
In short, as Nick says, the hot spot is not a prediction of GHG driven warming, it is a predicted result (from climate models) of any surface warming. That we have had difficulty observing this hotspot speaks more to observational challenges than it does to any flaw in the physics of the radiative greenhouse effect (because we know for a fact that the surface is warming).
A much more direct prediction of GHG-driven warming is cooling of the stratosphere, and this is something that has been observed:
Link to Sherwood, 2015, cited in the video, showing evidence of the existence of the tropospheric hot spot:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-9326/10/5/054007
From your link.
“”””Second, as shown in previous studies, tropospheric warming does not reach quite as high in the tropics and subtropics as predicted in typical models. “”””
The models are still incorrect.
Lol ok, so the models don’t perfectly capture the nature of the hotspot, but the hot spot is there (and largely consistent with modeled results). So the argument that the hot spot doesn’t exist is quite wrong. More importantly, the hot spot is not a prediction of GHG-driven warming, but of any forced surface warming. The direct prediction of GHG-driven warming is cooling of the stratosphere, which has been observed.
Moving the goalpost again I see, the reality is that the models are still incorrect.
LOL, it is clear you are easily mislead by that crap of a paper the NOAA to this day doesn’t acknowledge that lie as the data still shows negligible warming in one layer and a slight COOLING in the other layer.
From climate4you, scroll 3/4 of the way down to reach the section I quoted from,
LINK
===
It has been effectively addressed here in this LINK showing how he plays statistical games to make his lie.
If you wish to reject the Sherwood paper, you’re just back to the state of having radiosonde data that is too uncertain to show you anything whatsoever about trends in the troposphere, you haven’t disproved the existence of the tropospheric hotspot.
And, let’s say it again until it starts to sink in, the tropospheric hotspot is not a prediction of GHG-driven warming, it is a predicted result of any forced surface warming. We know for a fact that the surface is warming, so if we don’t see the hotspot it is most likely an issue with our observational data (it could also be that there simply shouldn’t be a hot spot under force surface warming and that the models have that wrong, but the prediction follows some pretty basic physics so that is also unlikely).
LOL, so you can’t defend the paper, why don’t you say that and stop being a fool.
You wrote this contradictory mess:
You should stop before you hurt yourself.
I’m not attempting to “defend” the paper, the paper exists, the authors did careful analysis of the radiosonde data, tried to rectify some of its many inconsistencies, and published the results. If you reject the paper you’re just back at the state of not being able to establish any trend with the radiosonde data, it doesn’t mean you have proven the contra-result. I understand that you are probably struggling to grasp this concept, so I’m happy to keep repeating it for you until you’ve had enough time to wrap your head around it.
I see you’re also confused here as well. Not to worry, I can help you work it out. If there is any agent forcing the surface to warm, climate models say it will produce a tropospheric hot spot. It doesn’t matter if the forcing is CO2 or an increase in solar output (or something other mechanism), as long as there is forced surface warming (i.e. not from internal variability), you’ll get the hot spot. So when people say, “if there is no hot spot it means CO2 is not a greenhouse gas,” they are simply mistaken and are making a logically incoherent argument.
At best you could try to argue that if there is no hot spot it means there is no surface warming occurring, but that argument fails because we know for a fact that there is surface warming occurring. It could also be that the models are wrong that there should be a hot spot at all, but the physics leading the models to produce the hotspot are well understood, so that also isn’t a probable explanation. So the likeliest explanation is that there are deficiencies in our observations of tropospheric temperature trends, which we know that there are because we know there are glaring issues with the radiosonde data.
Sherwood et al. tried to rectify some of those issues, but if you reject their approach then you’re just left with the glaring holes in the radiosonde data, so that doesn’t help your argument.
You really endorse this stupid statement by Sherwood?
LOLOLOLOLOLOLOL!!!
You didn’t address anything I posted thus you have nothing to show for and it has been addressed a number of times 8 years ago which is why only a few remaining warmists/alarmists like YOU still talk about it while the NOAA never accepted it.
It is clear you have NOTHING to offer on this worn out lie YOU are promoting.
I’m not interested in arguing about the Sherwood paper, I present it as an example of a study that attempted to resolve the glaring issues in the radiosonde data, and found that the hot spot emerged when they did. The points I am interested in are the ones you seem to be blithely ignoring – that the hot spot is not a prediction of AGW, and any absence of observations is far more likely to be the product of observational deficiencies than it is the absence of the hot spot itself.
Again, here are two climate model runs, one forced with GHGs and the other with just solar forcing:
Play spot the difference for a moment.
Once again to point what you keep ignoring the NOAA doesn’t accept Sherwood Radiosonde claims because they are not legitimate data changes.
You also ducking his words which are stupid:
That is the REALITY you keep fighting.
The AGW conjecture is the pseudoscientist basis for everything regarding the CO2 effect thus your word games are a waste of time as you are now LYING as part of your goalpost moving.
You can stop LYING now since AGW hypothesis covers everything via CO2 and other GH gases claimed as a major cause of warming.
AlanJ writes
“And, let’s say it again until it starts to sink in, the tropospheric hotspot is not a prediction of GHG-driven warming, it is a predicted result of any forced surface warming.”
The models predict the degree to which the hotspot changes and they get it wrong. That means they get the energy available for evaporation wrong and the interactions in the atmosphere wrong. It’s not rocket science.
You can’t dismiss this feature of them whilst still retaining any confidence they’re modelling climate change. Well…you might be able to do it but I’m not that naive.
This was addressed right here in this blog 8 years ago:
LINK
My comment on this in 2015, LINK
Peter Miller who was a student under Professor Kridge talks about the Kridging method that Sherwood misused to create his bogus claims, LINK
bolding mine
AlanJ wites
Sherwood is one of those “scientists” who’s findings can reasonably be ignored. He couldn’t be any more biased. His earlier paper using wind data as a proxy for temperature to find the hotspot instead of the temperature reading on the very same radiosonde excludes him as an individual interested in finding the truth.
We can’t see it but we believe it exists.
That’s religion for ya.
… the simplified and massively “parameterised” implementation(s) found in the model code being wrong, even if the “fundamental physics” equations are correct.
Remember Richard Feynman’s “old fashioned / historic” summary of “The Scientific Method” (TSM) :
_ _ _ _ _
In the early-2000s there was much talk of higher-resolution climate models finding a “fingerprint” in their output “latitude-altitude warming rate” X-Y plots that would better match the balloon (radiosonde, from 1958) and satellite (MSU, from 1979) datasets.
There was even hope that they could (eventually, with a fine enough grid resolution) get the exact numbers output by future climate models, in “degrees Celsius per decade / century”, to agree with the historical empirical observations.
As it became clear that the “details” were never going to match up, the “fingerprint” was dumbed-down to the numberless :
“The troposphere will warm, the stratosphere will cool.”
_ _ _ _ _
… oh dear …
… the Sherwood et al (2015) paper with the full title “Atmospheric changes through 2012 as shown by iteratively homogenized radiosonde temperature and wind data (IUKv2)” …
… the one where they tried to apply “correction” using data from the “wind vector” sensor to the data from the scientific instrument specifically designed to measure temperature …
… the one where applying “homogenisation” to data from neighbouring stations wasn’t just done once, but “iteratively” …
I have seen (very) similar procedures referred to as “torturing the data until it confesses”.
_ _ _ _ _
A copy of Figure 1 from Sherwood et al is attached below (to avoid people having to switch between tabs in their browsers), but note that it has the South Pole (-90) on the left of the graph while AR4 Figure 9.1 has the South Pole (90S) on the right of each panel.
Take the time to carefully compare it to “Panel f : The sum of all forcings” in AR4 Figure 9.1 above …
… and note how the “fastest warming” occurs in zones “5°S-15°N, 300-150 hPa plus 25-30°S, 600-200 hPa” for Sherwood et al, but only in the “30°N-30°S, 500-150 hPa” zone in Figure 9.1(f).
“If it disagrees with experiment, it’s wrong. That’s all there is to it.”
Yeah, Sherwood papers are a mess it is a mystery anyone still thinks he is a good researcher when he cheats and make up numbers.
gator69 writes back in 2015 here in this blog LINK:
HAW HAW HAW HAW HAW, how can anyone still think Sherwoods paper is better than bird cage quality?
The NOAA where the Radiosonde data is located has NOT been updated using Sherwood’s made-up numbers thus his paper didn’t improve anything except to excite a few remaining warmists/alarmists morons who are easy to fool.
LINK
Yep, what it does probe is the lack validity of the Models! Thanks genius
Nick writes
“That is normally understood to be the extra warming at the surface produced by GHGs.”
I think the focus is on CO2 impacting the greenhouse effect which does start at the TOA?
“That is normally understood to be the extra warming at the surface produced by GHGs”
Atmospheric warming by human CO2 has NEVER been observed or measured anywhere on the planet.
Someone’s “understanding” is more like fairytale imagination.
Please describe in detail the necessary observations that would have to be made to convince you that warming driven by anthropogenic emissions of CO2 does exist.
Warming does occur. How much is debatable. Esteemed radiation experts like Soon and Happer say CO2 is saturated. Just in case some don’t know, that doesn’t mean more CO2 will absorb more, it means current CO2 concentration absorbs practically all of the radiation available. Adding more CO2 will not increase the radiation from the surface therefore, additional CO2 will have little effect. That is why doubling has an logarithmic reduction in heating capacity.
Happer claims that doubling the concentration of CO2 will produce >2 degrees of warming, not sure where you got this incorrect notion.
I notice you did not mention the saturation factor.
Here is a paper from Berkeley about the logarithmic forcing.
Remember concentration must double for every increase, that is logarithmic.
100 ->200 +100 4°
200->400 +200 4°
400->800 +400 4°
800->1600 +800 4°
But that ignores the saturation effect. Where does the radiated energy to achieve the 4° come from if CO2 is saturated already?
You should ask Happer that question, as it’s his calculations you are referencing.
If I understand the gist of H&W’s paper correctly, they are repeating line by line radiative transfer calculations from Manabe and Wetherald in the 60s with an updated spectral lines database. Their references to “saturation” are talking about the per-molecule attenuation – essentially that radiation is mostly absorbed close to the ground. That doesn’t tell you what the forcing is going to be, because that relies on the transfer of radiation through each layer of the atmosphere. When H&W calculate this, they find a sensitivity of >2 degrees C:
You have no idea about energy transfer do you?
If a CO2 molecule close to the ground absorbs IR and then emits it to a higher altitude CO2 molecule, it loses energy. If it collides with an H2O, N2, or O2, it loses energy. It isn’t additive. Energy is transferred, not created.
Once saturation is reached adding more CO2 only decreases the probability of any individual CO2 molecule intercepting IR at a CO2 frequency.
What matters is that the energy is absorbed and re-emitted at altitude. Adding more CO2 will always raise the effective height of emission (how far energy needs to travel before it can be radiated away to space). So you can be at a point of saturation (or near saturation) near the ground for the bands relevant to CO2, but you will never reach a point where the upper atmosphere is saturated.
Thanks, Nick. The canonical definition, as you point out, is to subtract TOA LW from surface LW.
The problem is that the amplitude of TOA LW is not a simple function of GHGs. Instead, TOA LW is some function of GHGs, sensible/latent heat flux, and atmospheric solar absorption. And one-third of the total atmospheric energy flux is NOT from surface LW.
As a result, we’ll see constant changes in TOA LW even if there is zero change in GHGs … which kinda screws up the Ramanathan measurement.
w.
It has seemed to me that the first question of interest is to measure total radiation entering the atmosphere and the subtract from it total radiation leaving the atmosphere.
A positive number would indicate the Earth system as a whole is warming. A negative number would be cooling.
Of course the data would need to be averaged over both the day/night cycles and season or annual cycles. Also perhaps some consideration of energy produced by radioactive decay, eg in the Earth’s core, might be relevant at the margin.
Perhaps simplistic, but if the alarmists cannot show a net positive number, then the Earth is not warming.
Add to factors to be considered the different incoming and outgoing radiation levels at various places eg tropics v poles.
I posted the CERES net flux here.
The eminent hydrologist Demetris Koutsoyiannis has a new paper On Hens, Eggs, Temperatures and CO2: Causal Links in Earth’s Atmosphere
H/T Pierre L. Gosselin New Study: The Rising-CO2-Causes-Warming Perception Not Supported By Real-World Observation
The Koutsoyiannis paper is interesting. It reminds me of the cointegration work that Beenstock et al performed on CO2 and Temperature that also went against the consensus assumption of causality:
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Polynomial-cointegration-tests-of-anthropogenic-on-Beenstock-Reingewertz/845d27e46ff475300ffcccc4978bc3d578e72b68
In short, there’s a huge body of work that debunks the CO2 ‘control knob’ paradigm that has been systematically suppressed.
As I have mentioned before, a change in CO2, with the resulting change in the downwelling radiation, has no effect on the energy imbalance. The energy imbalance is independent of changes in the downwelling radiation, at least to a first order approximation.
maybe, just maybe we are using flawed input data (of course we are) … making assumptions about gasses (that they are well mixed when the satellites prove they ARE NOT) … and trying to apply laboratory experiments to the entire planet (ahh, not a good idea) …
sure we can make alot of fancy charts … but GIGO dooms the effort …