GUEST: HENRIK SVENSMARK
By bombarding the Earth with cosmic rays and being a driving force behind cloud formations, the sun plays a much larger role on climate than “consensus scientists” care to admit.

The Danish National Space Institute’s Dr. Henrik Svensmark has assembled a powerful array of data and evidence in his recent study, Force Majeure the Sun’s Large Role in Climate Change.
The study shows that throughout history and now, the sun plays a powerful role in climate change. Solar activity impacts cosmic rays which are tied to cloud formation. Clouds, their abundance or dearth, directly affects the earth’s climate.
Climate models don’t accurately account for the role of clouds or solar activity in climate change, with the result they assume the earth is much more sensitive to greenhouse gas levels than it is. Unfortunately, the impact of clouds and the sun on climate are understudied because climate science has become so politicized.
Full audio interview here:
H. Sterling Burnett, Ph.D. is a Heartland senior fellow on environmental policy and the managing editor of Environment & Climate News.
Discover more from Watts Up With That?
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Thought we already knew that, courtesy of Dr. Svensmark. Good to see it repeated; maybe some new people will become more comfortable with the world not ending because of beneficial warming.
The interviewer should have asked Svensmark about the results of the CLOUD experiment at CERN by Kirby and team. The CLOUD experiment seems to indicate that the modulation of cosmic rays by the sun’s magnetic field does not produce a significant enough effect to influence the climate substantially.
It would have been really interesting to hear his views on the results of the CLOUD experiment.
Thats not an accurate synopsis of the CLOUD results. CLOUD determined that GCRs on their own did not create droplets, NOT that they weren’t part of the process. CLOUD showed that there was another catalyst that worked with GCR to form droplets.
Please expand on that last sentence and provide a link to the CLOUD experiment.
The link to Svensmark’s paper included in the article above is what you need. Specifically, when you get to page 15, you’ll have your answer.
However, don’t just jump to page 15 and start reading there. You have to read the preceding pages to understand.
Dunne et al 2016, “Global atmospheric particle formation from CERN CLOUD measurements”
“in the present-day atmosphere, cosmic ray intensity cannot meaningfully affect climate via nucleation”
http://science.sciencemag.org/content/354/6316/1119
Frederick Michael The 2011 Kirkby paper has been superseded by many others showing little significance between GCR and climate change.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1308.5067
http://science.sciencemag.org/content/354/6316/1119
https://www.swsc-journal.org/articles/swsc/abs/2012/01/swsc120049/swsc120049.html
As early as October 2011 Jasper Kirkby made a presentation at CERN in which he indicated that the droplets were too small to result in cloud formation.
Frederick Michael Kirkby’s October 2011 presentation at CERN
“Freshly-nucleated aerosol particles are far too small to seed cloud
droplets”
page 26.
The link to Kirkby’s presentation:
https://indico.cern.ch/event/158340/attachments/178006/250385/kirkby_cern_colloquium_13OCT11.pdf
Maybe, but I prefer this solution:
http://joannenova.com.au/2015/01/is-the-sun-driving-ozone-and-changing-the-climate/
because I’m not convinced that more condensation nuclei per se is sufficient to create the observed system response to solar variations.
I agree there is certainly more going on than cloud cover changes only, as resulting directly from increased CCN’s as a consequence of more comics rays.
Further to your summarised explanation, I see the ozone layer warming and expanding the stratosphere/mesosphere in a particular way by means of changing the intensity, position and orientation of the Hadley Cells and the Azores High in particular. (Haigh) Recent decades and high sun activity has seen the Azores High often positioned to force the predominately zonal SW to NE jet-stream across the North Atlantic to the north of Norway, or thereabouts and increasing water vapour values and cloud cover in NW Europe/Asia: This in late autumn/winter/early spring inhibits surface temperatures from dropping and the formation of snow cover. A sustained period of a SW to NE jet-stream flow, imo, also increases the momentum and penetration of the Gulf-Stream/North Atlantic Drift into the Arctic basin with rising sea temperatures, increased cloud cover and associated ice loss.
Then you have to consider the knock on effects of the changed synoptics in NW Europe across the N. hemisphere…….
I agree there is certainly more going on than cloud cover changes only, as resulting directly from increased CCN’s as a consequence of more comics rays.
Further to your summarised explanation, I see the ozone layer warming and expanding the stratosphere/mesosphere in a particular way by means of changing the intensity, position and orientation of the Hadley Cells and the Azores High in particular. (Haigh) Recent decades has seen high sun activity with the Azores High often positioned to force the predominately zonal Jet-stream SW to NE across the North Atlantic to the north of Norway, or thereabouts and increasing water vapour values and cloud cover in NW Europe/Asia: This in late autumn/winter/early spring inhibits surface temperatures from dropping and the formation of snow cover. A sustained period of zonal jet-stream, imo, also increases the momentum and penetration of the Gulf-Stream/North Atlantic Drift into the Arctic basin with rising sea temperatures, increased cloud cover and associated ice loss.
Then you have to consider the knock on effects of the changed synoptics in NW Europe across the N. hemisphere…….
Exactly
It’s not necessarily an either/or situation. They could both be playing a role.
How ?
I agree. Changing UV causes changing weather patterns.
Ahhh; anyone heard of the Wilson cloud chamber? It was far more than a scientific curiosity, it worked so well that it was a mainstay tool of nuclear physics in the 1970’s – creating pictures of nuclear particle interactions which were photographed and analysed. Lots of high school students used to make them as science projects (me included) and I can testify from personal experience that it makes cosmic rays visible as vapour trails ie: condensation nuclei large enough to easily see with the naked eye which means round the same sort of droplet size as exist in clouds.
I do recall that and the condensation tracks dissipated as fast as they formed.
To have the observed effects on climate cosmic rays need to alter the gradient of tropopause height between equator and poles.
Do you have a mechanism for that ?
Guess he has a point!
Would like some connection to SO2 emissions.
As shown in the picture figure 11 the clouds are formed after boat tracks filled with SO2 emissions.
SO2 emissions have nearly gone down to zero as less clouds forms.
Nope they don’t like it . . .
In a detailed 2013 post on the scientists’ blog RealClimate, Rasmus E. Benestad presented arguments for considering Svensmark’s claims to be “wildly exaggerated”. (Time magazine has characterized the main purpose of this blog as a “straightforward presentation of the physical evidence for global warming”.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Henrik_Svensmark
But Time is a fully paid up member of the consensus and thus has no credibility in rating anything having to do with communication about the climate.
RealClimate is little more than a propaganda site the refuses to print anything that doesn’t support the claim that CO2 is the main driver of climate.
Personally I think if there were a breakthrough that allowed scientists generally to confirm a major new natural influence on climate you’d absolutely read about it in RC and eventually Time.
The evidence for Svensmark theory comes mainly from Svensmark (supporters & others mostly non-scientists claim to ‘confirm’ it doing similar solar curve fitting, but that’s mainly adjusting data until there is correlation and then claiming that as evidence of causation.)
* CERN CLOUD experiment says “in the present-day atmosphere, cosmic ray intensity cannot meaningfully affect climate via nucleation”
* Other scientists looking for the correlation Svensmark claims find “no statistically significant correlations between cosmic rays and global albedo or globally averaged cloud height, and no evidence for any regional or lagged correlations” and so on.
* Physically it doesn’t make a lot of sense – “A bigger issue is the number of such particles [which] would be negligible compared with the background aerosol and the aerosol humans are adding by burning things, tilling soil, etc… If clouds were affected by cosmic rays they would have been affected a hundred times more strongly by human air pollution, and the world would have cooled over the past century, rather than warmed.”
* IPCC concluded “No robust association between changes in cosmic rays and cloudiness has been identified”
The basis of Svensmark hypothesis is variability of the heliospheric magnetic field at the heliopose.
However changes in the strength of the Earth’s magnetic dipole is by far greater and (as my findings show) has strong correlation with the changes in the global temperature data.
http://www.vukcevic.co.uk/CT4-GMF.htm
There seems to be a strong correlation, but do you have a link to an article, suitable for a lay person, which explains how the one might cause the other?
No. It’s my own hypothesis, I’m working on a plausible mechanism but the progress is slow, hopefully I might eventually get there.
p.s. apologies to all readers for the spelling errors, the above is posted from a small hend held android and editing is a menace.
You need to switch to an iPhone where its autocorrect will spell everything correctly, but change the words you write to something completely different than what you intended.
:<)
Autocorrect is your enema!!
Android, or at least Samsung Android does that.
All Androids do it as well.
rb, Hahahahaha!
Indeed the iPhone will change the words resulting in some very cryptic messages.
I’ve been successfully doing at least half of that all by myself for several decades already.
Twenty years ago everyone assumed that the geomagnetic field changes where slow over thousands of years and that large geomagnetic changes were every 200,000 years, not every 2400 years.
In the last 15 years the geomagnetic field specialists have discovered that the geomagnetic field changes cyclically and that the cyclic changes in the geomagnetic field correlate with climate change.
They have also found evidence of extraordinary large and fast changes to the geomagnetic field that occurred in years.
The paradox is what is causing large periodic changes to the geomagnetic field?
This finding (cyclic large changes to the geomagnetic field) is akin to the finding the tectonic plates are moving.
There was a delay in accepting the tectonic plates are moving observations as there was and still is no mechanism to move the tectonic plates. The change in the geomagnetic field is orientation, the poles abruptly move and abrupt changes to the magnetic field intensity, including frequent geomagnetic excursions.
http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/416/1/gubbinsd4.pdf
Is the geodynamo process intrinsically unstable?
Recent palaeomagnetic studies suggest that excursions of the geomagnetic field, during which the intensity drops suddenly by a factor of 5 to 10 and the local direction changes dramatically, are more common than previously expected. The `normal’ state of the geomagnetic field, dominated by an axial dipole, seems to be interrupted every 30 to 100 kyr; it may not therefore be as stable as we thought. We have investigated a possible mechanism for the instability of the geodynamo by calculating the critical Rayleigh number (Rc) for the onset of convection in a rotating spherical shell permeated by an imposed magnetic field with both toroidal and poloidal components.
Recent studies suggest that the Earth’s magnetic field has fallen dramatically in magnitude and changed direction repeatedly since the last reversal 700 kyr ago (Langereis et al. 1997; Lund et al. 1998). These important results paint a rather different picture of the long-term behaviour of the field from the conventional one of a steady dipole reversing at random intervals: instead, the field appears to spend up to 20 per cent of its time in a weak, non-dipole state (Lund et al. 1998). One of us (Gubbins 1999) has suggested that this is evidence of a rapid natural timescale (500 yr) in the outer core, and that the magnetic field is usually prevented from reversing completely by the longer diffusion time of the inner core (2 to 5 kyr). This raises a number of important but difficult questions for geodynamo theory. How can the geomagnetic field change so rapidly and dramatically? Can slight variations of the geomagnetic field affect the dynamics of core convection significantly? If so, is the geodynamo process intrinsically unstable?
http://sciences.blogs.liberation.fr/home/files/Courtillot07EPSL.pdf
Are there connections between the Earth’s magnetic
field and climate? Vincent Courtillot, Yves Gallet, Jean-Louis Le Mouël,
Frédéric Fluteau, Agnès Genevey
We review evidence for correlations which could suggest such (causal or non-causal) connections at various time scales (recent secular variation approx 10–100 yr, historical and archeomagnetic change appox. 100–5000 yr, and excursions and reversals approx. 10^3–10^6 yr), and attempt to suggest mechanisms. Evidence for correlations, which invoke Milankovic forcing in the core, either directly or through changes in ice distribution and moments of inertia of the Earth, is still tenuous.
Correlation between decadal changes in amplitude of geomagnetic variations of external origin, solar irradiance and global temperature is stronger. It suggests that solar irradiance could have been a major forcing function of climate until the mid-1980s, when “anomalous” warming becomes apparent. The most intriguing feature may be the recently proposed archeomagnetic jerks, i.e. fairly abrupt (approx. 100 yr long) geomagnetic field variations found at irregular intervals over the past few millennia, using the archeological record from Europe to the Middle East.
These seem to correlate with significant climatic events in the eastern North Atlantic region. A proposed mechanism involves variations in the geometry of the geomagnetic field (f.i. tilt of the dipole to lower latitudes), resulting in enhanced cosmic-ray induced nucleation of clouds. No forcing factor, be it changes in CO2 concentration in the atmosphere or changes in cosmic ray flux modulated by solar activity and geomagnetism, or possibly other factors, can at present be neglected or shown to be the overwhelming single driver of climate change in past centuries. Intensive data acquisition is required to further probe indications that the Earth’s and Sun’s magnetic fields may have significant bearing on climate change at certain time scales.
http://geosci.uchicago.edu/~rtp1/BardPapers/responseCourtillotEPSL07.pdf
Response to Comment on “Are there connections between Earth’s magnetic field and climate?, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 253, 328–339, 2007” by Bard, E., and Delaygue, M., Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., in press, 2007
Also, we wish to recall that evidence of a correlation between archeomagnetic jerks and
cooling events (in a region extending from the eastern North Atlantic to the Middle East) now covers a period of 5 millenia and involves 10 events (see f.i. Figure 1 of Gallet and Genevey, 2007). The climatic record uses a combination of results from Bond et al (2001), history of Swiss glaciers (Holzhauser et al, 2005) and historical accounts reviewed by Le Roy Ladurie (2004). Recent high-resolution paleomagnetic records (e.g. Snowball and Sandgren, 2004; St-Onge et al., 2003) and global geomagnetic field modeling (Korte and Constable, 2006) support the idea that part of the centennial-scale fluctuations in 14C production may have been influenced by previously unmodeled rapid dipole field variations. In any case, the relationship between climate, the Sun and the geomagnetic field could be more complex than previously imagined. And the previous points allow the possibility for some connection between the geomagnetic field and climate over these time scales.
http://geosci.uchicago.edu/~rtp1/BardPapers/responseCourtillotEPSL07.pdf
Response to Comment on “Are there connections between Earth’s magnetic field and climate?, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 253, 328–339, 2007” by Bard, E., and Delaygue, M., Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., in press, 2007
Cosmic rays and cloud formation who would have thunk it.
Solar activity has been quite steady over the last 300 years: its variation does not match that of the climate very well, so observationally there is not much support for the notion that “the sun plays a powerful role in climate change”.
Hi doc, nice to hear from you again, hope all is well.
For about a week the daily SSN count has been above average
[deleted] EISN_current-3.txt
do you think the SC24 has still some time to go; and if so when do you expect it’s minimum or to be more precise SC24-25 crossover?
Thanks.
Hi doc, nice to hear from you again, hope all is well.
For about a week the daily SSN count has been above average
[deleted link per request] … EISN_current-3.txt
do you think the SC24 has still some time to go; and if so when do you expect it’s minimum or to be more precise SC24-25 crossover?
Thanks
URLs that start with file:// don’t help those of us without direct access to your computer. 🙂
Hi there
Sorry about it somehow I posted copy of downloaded file rather than the source. I’m about thousand miles away from my desktop, the file is on my mobile android hand held.
FOR Attention of moderator:
Would you be so kind to delete the entry in my comment above
vukcevic May 10, 2019 at 2:58 am
which might be a security risk. Thanks.
There’s no security risk, your computer is not identifiable from that mangled URL.
Thanks Mr. Watts.
I think you’re talking about TSI, Leif. That’s not what Svensmark is talking about.
He discusses it starting around 5 or 6 minutes into the recording.
Most of what I read ties magnetic influences to ‘solar activity’ which is usually tied to sunspots and TSI. Isn’t it expected that the main effect is correlated with activity (higher solar activity -> less cosmic rays -> fewer clouds -> warmer), and therefore the effect has the same problem as TSI explanations, namely a flat or declining trend while the world warms?
Maybe the thought is for TSI we *know* the variations are too small, because radiation is energy which translates directly to temp. But really GCR theory has this same problem. Though clear physics tying them to global temp haven’t been identified, the evaluations done on the hypothesized effect (on clouds) find it a couple of orders of magnitude too small at best, similar to TSI variability being too small.
Very funny. From the depths of the Maunder Grand Minimum to the heights of the Modern Maximum. It is difficult to find more variability than that in just three centuries in the Holocene record.
“From the depths of the Maunder Grand Minimum to the heights of the Modern Maximum. It is difficult to find more variability than that in just three centuries in the Holocene record.”
Looks like just a little over 1 W/m^2 at the extremeon Leif’s plot
That’s not even 0.1%.
“quite steady” covers it pretty well I’d say.
AB
What if you calculated the 300-year average and then presented the annual ‘anomalies,’ as is commonly done with temperatures? Do you suppose it would still look “quite steady?”
How would the TSI anomalies compare to the temperature anomalies?
Hi Anthony,
You are thinking TSI. Svensmark is talking about magnetic activity. Not the same. I suggest you actually try and understand Svensmark’s research before dismissing it with inapplicable data.
The theoretical basis for the work has been done by Nir Shaviv (2008). That’s also worth looking at.
Cheers !
Apparently you have trouble with the concept of Solar Grand Minimum. We are not in one. And the Modern Maximum, well recognized in the scientific literature is just the opposite to one.
What characterizes the Modern Maximum (honest question)?
“The new correction of the sunspot number, called the Sunspot Number Version 2.0, led by Frédéric Clette (Director of the World Data Centre [WDC]–SILSO), Ed Cliver (National Solar Observatory) and Leif Svalgaard (Stanford University, California, USA), nullifies the claim that there has been a Modern Grand Maximum… The new record has no significant long-term upward trend in solar activity since 1700, as was previously indicated… ”
http://www.iau.org/news/pressreleases/detail/iau1508/
In any case it sounds like you dispute the mainstream view on the impact of a Grand Minimum. Just restating Svensmark or some other dispute?
Jones et al 2011, “What influence will future solar activity changes over the 21st century have on projected global near-surface temperature changes?”
“Even in the event of the Sun entering a new Maunder Minimum like activity state the climate response is very small compared to the projected warming due to anthropogenic influences”
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2011JD017013
Feulner and Rahmstorf 2010, “On the effect of a new grand minimum of solar activity on the future climate on Earth”
“Here we use a coupled climate model to explore the effect of a 21st‐century grand minimum on future global temperatures, finding a moderate temperature offset of no more than −0.3°C in the year 2100 relative to a scenario with solar activity similar to recent decades. This temperature decrease is much smaller than the warming expected from anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions by the end of the century”
http://www.pik-potsdam.de/~stefan/Publications/Journals/feulner_rahmstorf_2010.pdf
Gray et al 2009, “Solar Influences on Climate”
“Despite these uncertainties in solar radiative forcing, they are nevertheless much smaller than the estimated radiative forcing due to anthropogenic changes, and the predicted SC‐related surface temperature change is small relative to anthropogenic changes.”
http://solar-center.stanford.edu/sun-on-earth/2009RG000282.pdf
Leif, it always helps reading the material or even the outline before commenting.
Solar activity in this context consists of the changing magnetic fields and the resulting modulation of cosmic rays in the heliosphere. Figure 5 show three measurement of galactic cosmic rays. Δ 14C, Δ10Be, (Delaygue and Bard 2011), Δ10Be ( Beer et al. 1994)
Where is the “steadiness” here? Not saying Svenmark is right but playing a role does not equal some direct causation of radiation hitting the planet. As such your reply appeared like a classic straw man.
John Dowser May 10, 2019 at 1:26 pm
“Leif, it always helps reading the material or even the outline before commenting.”
DR. Leif Svalgaard is well versed on the subject.
He has been following Dr. Svensmark work since he first publish a paper on the subject of cosmic rays and cloud formation.
John, the Doc is the go to person on astrophysics, he was involved with the solar cycle reconstruct.
Agree or not, with him but don’t make the mistake of thinking he does not know the subject matter.
Michael
So summer and winter is not proof enough of the role tge sun plays??? No models…all observations.
Axial tilt causes the seasons, not solar output.
Without solar output axial tilt would be meaningless.
Cart before horse much?
“Without solar output ” strawman much?
Solar denier?
Tell me Jack, what is the main driver of Earth’s climate? Are we not discussing climate change on Earth? And why do you deny it’s ability to alter climate?
Try tilting your head. Did it change temperature?
Solar output varies 0.1%. It has little to do the climate change. Historically the main driver of climate was Milankovitch cycles, according to which we should be cooling.
http://ossfoundation.us/projects/environment/global-warming/milankovitch-cycles
Milankovich? How does a Milankovitch Cycle change climate without the Sun?
Why are you a solar denier? .1% of a very large number is also a very large number. CO2 cultists claim that a change of .15% in greenhouse gases will lead to runaway warming. Do you know to what CO2 responds to produce warming? Is it tilt?
Leif Svalgard: “ not much support for the notion that the sun plays a powerful role in climate change”.
Svensmark’s report emphasizes the indirect effect of solar variation on cosmic ray penetration and formation of nuclei for cloud condensation. The effect is estimated at about 1.2W/m^2 at the surface over the solarcycle, which does not look to me like “force majeur”, but is about the same order of magnitude as estimates of the CO2 effect. He accepts that TSI variation is much smaller than that.
The paper clearly needs better editing since it many places starting from the abstract it is clearly
wrong. For example the statement “ An important scientific task has been to quantify the solar impact on climate, and it has been found that over the eleven- year solar cycle the energy that enters the Earth’s system is of the order of 1.0–1.5 W/m2.“ is clearly wrong. I am guessing this is a translation error but it does not
inspire confidence in the report. Similarly for example the claim is made that the temperature difference between the medieval warm period and the little ice age was between 1 and 1.5 degrees yet Fig. 5 only shows a temperature difference of about 0.5 degrees.
“At the surface it is only 0.2 W/m2 (over a solar cycle), after taking geometry and albedo into account…”
Becomes – Force Majeure the Sun’s Large Role in Climate Change – in the title.
Really? Clutching at straws.
Que? dunno where that quote is from but any solar panel will net you a peak of 1KW/sq m and an average of around 100W/sq m.
Except at polar latitudes.
From Svensmark’s study. Thats the huge variation over 11 years.
The title should have been:
Force Minore, the Sun’s almost negliglble Role in Climate Change
That’s funny! The Sun has a nearly negligible role in climate change? Ever heard of Summer or Winter? LOL
Ever heard of axial tilt? That is what causes summer, fall, winter and spring. The solar output is pretty constant; it varies about 0.1%
The Sun has nothing to do with Summer or Winter? Really LOL
It isn’t the “tilt” that changes the seasons, it is the angle of the Sun. Without the Sun your tilt would be meaningless.
How have people become so ignorant?
[?? .mod]
Gator
I regret that your plain text on the Internet cannot convey whether you are being sarcastic or not.
Nevertheless, let us assume you mean your exact words.
No, your statement is not true.
The earth rotates about the sun in a elliptical orbit. The plane of that elipse defines a “flat surface.”
Now, five DIFFERENT things happen on that ecliptical plane that control the angle of the sun each hour, which controls how much solar radiation is available at the earth’s surface – and it’s easy to mix them up because they ALL happen at the same time at various different rates ALL year long: Only the first impact is independent of solar elevation angle. The other four affect solar elevation angle, not Top of Atmosphere radiation levels available.
First TOA radiation changes. The distance between the earth and the sun changes through the year because the earth’s orbit is an ellipse, not a circle. This fact changes the amount of radiation that is received at Top of Atmosphere above every sq kilometer on the earth’s surface every day of the year. (The ellipse major and minor values changes very slowly over the course of tens of thousands of years, but this change can be ignored when looking at only a few hundred or a few thousands of years.)
Second, the earth rotates about its own axis once per day. This means that, on every day of the year, at every latitude on earth, the sun’s solar elevation angle changes every hour of every day. (Well, technically, every second of every minute of every hour of every day of the year, but let’s not get too picky about details that can be easily calculated and accurately predicted.) In the Arctic and Antarctic regions, the Air Mass calculation is NOT correct by assuming the atmosphere is a constant thickness; it is also NOT correct by assuming the atmosphere is “flat”, and it is NOT correct assuming there is no diffraction. Properly calculated though, an adequately correct Air Mass can be predicted for every solar elevation angle of every minute of every hour of every day of the year for every altitude and latitude of every kilometer on earth.
Third, the earth is a sphere. Even if the earth had no atmosphere, and even if the earth had no axial tilt at all, the radiation at ground level/sea level on each square meter will vary by the sine of the incoming solar energy at every different solar elevation angle. Over the course of a full year, the far north and far south latitudes will NEVER receive the same average radiation on the ground as the mid-latitudes and tropics.
Fourth, the earth’s atmosphere is made up of a constantly varying series of layers each layer which has different atmosphere attenuation factors, different individual thicknesses, different average and total pressures, different relative humidities, different dust and pollen and particulate content, and different cloud/diffusion coefficients. In general though, the atmosphere can be approximated as a single “layer” above the earth, but the specific differences between layer content and layer thickness and temperatures changes over the course of a year. Atmosphere conditions in January are different than March, April is different than August, September different from November – EVEN IF the solar elevation angle at any given moment is identical with the previous day, previous month, or previous season. (We will ignore for a moment the effect of a change in local altitude in local solar ground radiation per square kilometer.)
Fifth, the earth axis IS tilted at 23.45 degrees with respect to the ecliptic plane. (This tilt value changes very slowly over the course of tens of thousands of years, but this change can be ignored when looking at only a few hundred years.) This means that, from October through February, the southern hemisphere receives much more solar radiation than the northern hemisphere. From April through August, the Northern hemisphere receives more sunlight energy than does the southern hemisphere.
RACookPE1978, I’m well aware of basic science. Are you?
How much difference would your points 1 through 5 make, if there were no Sun? This isn’t difficult, no need for a lengthy reply.
Gator
100%.
There is a direct and immediate change in Top Of Atmosphere solar radiation energy and TSI (Total Solar Irradiation).
Yes, a variation in TSI is critical. Yes, estimates in TSI change from solar cycle to solar cycle have been found, and they are by calculation roughly 1/3 of the estimated total effect of the change in CO2 levels blamed on human activity.
… the estimated total effect of the change in CO2 levels blamed on human activity.
And that says it all. Estimated. By the cult. The cult that denies natural climate change, the Sun, and the full effects of UHI, et al.
It’s quite obvious that you didn’t bother to read the article since it has nothing to do with TSI.
It has everything to do with TSI
As that is the modulating factor on cosmic rays……
Svensmark is talking about solar magnetic activity. That varies much more greatly than the TSI and affects the solar wind (particles more than radiation). Solar wind interacts with the cosmic ray flux.
You need to read Svensmark’s work properly, amigo.
Skepticalsins.
Oh.
TSI == Total Solar Irradiance.
I forget want the article said, but the report covers TSI and other possibilities. It points out why changes in TSI are not enough to cause the effects seen and goes into the math behind it in an appendix.
Please read the report, it’s not a peered reviewed journal paper, most everyone here can learn from it.
Svensmark. The Johnny Ramone of Climate Change. Turn the amp up to 11 and blow ’em away Henrik.
I read one of Roger Spencer’s books where he is of the view that nearly all 20th century warming could theoretically be explained by reduction in cloud cover related to the general increase in solar activity, which cloud cover has not been measured long enough to make a judgement.
I also caught Skeptical Science on the hop once, when they were talking about how the small variation in the 11 year cycle produces relatively large temperature effects, meaning climate sensistivity must be high- I pointed out that climate senstivity could be high for the sun and clouds but low for C02, which they suddenly realised could be true, but then just said that to have different sensitivities to different forcings ‘doesnt make sense’. It never occurred to them that cloud cover can throw all their nice ‘linear assumptions’ regarding different forcings out the window.
“Roger Spencer” !!
Do you mean Roy of the University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH)?
“… that nearly all 20th century warming could theoretically be explained by reduction in cloud cover related to the general increase in solar activity, which cloud cover has not been measured long enough to make a judgement.”
>>
Makes one wonder if the observed planetary ‘greening’ is not a combo of CO2 plus more photons striking ground level plants and planktonics due less % cloud cover (yet a more humid planet near ground level).
The Sun is more active now than over the last 8000 years:
https://www.mpg.de/research/sun-activity-high
Solar deniers couldn’t possibly have an agenda other than science. No, not possible.
Force Majeure, a well known legal escape clause in contracts, should now be applied to any Paris Accord, Carbon Tax Bill, extinction rebellion, etc.
Galactic Cosmic Ray flux and Solar modulation are totally outside any human control, thus voiding all the above.
I presume the title implies just this.
Just imagine, relativistic protons, CCN’s of a few nanometers, and aerosol droplets, have more climate action than all our combined autos, fires and factories. When we look at active galaxies, we should be glad ours is at least now quiet.
Did it tie in with these-
The .png is for New Mexico. The cosmic ray connection impacts low level maritime clouds and albedo. I don’t know if there’s a connection to NM droughts. Please go into more detail.
I was having fun at the expense of climate alarmism.
RE: First sentence.
I’m no cosmologist, but I thought Cosmic Radiation emanated from outside the Solar System and not from Sol. The interaction between solar output and the Earth’s magnetic field strengthens or weakens it leading to more or less cosmic radiation on the surface of the Earth and at higher altitudes. It’s why during solar minimums, airline crews are subject to a higher radiation exposure risk.
Yes, cosmic rays come from distant events. The idea is that changes in Sun’s magnetic field deflect cosmic rays and that when the field is stronger (active sun) fewer cosmic rays reach Earth. They don’t reach the surface, but muons from collisions high in the atmosphere do, and they are involved in creating the cloud condensation nuclei.
Active sun -> fewer cosmic rays -> fewer muons -> fewer CCN -> fewer clouds -> lower albedo -> global warming. I’ve left out several steps and other nuances involving sources of sulfur, clean air (few CCN), etc.
Cabin crews at 30,000ft a lot of the time get much more radiation exposure than landlubbers, and their health is intensively monitored. They actually benefit, its called Hormesis. Which is why the LNT, linear no-threshold radiation policy is not scientific. Life actually needs a certain amount of radiation.
The ISS astronauts got a nasty surprise a few years ago – cosmic radiation was ejecting neutrons from the metal skin into the vessel – they now carry neutron bubble detectors as far as I know.
Their orbit residency is likely a dose limit.
Your first paragraph also applies to radon gas in homes. The LNT was used, extrapolated from workers in uranium mines in Pennsylvania. Two different studies showed that there was a benefit for radon SLRDs in the 2-7 pCi/L range.
It’s probably not sufficient over a long period of time to believe the Sun is the single limiting factor in cosmic ray flux on Earth. While it is clear the solar wind can attenuate the levels of cosmic rays, implicit is the assumption the cosmic ray flux at heliopause is constant. Why should that be the case? Magnetic fields exist in the galaxy and can concentrate charged particles. If the solar system passes into a stream of higher density, the flux could rise for perhaps some extended period of time. We do not yet have the ability to observe particle density (high energy cosmic rays) in interstellar space. However, estimates of average galactic magnetic field strength suggest cosmic rays pass in straight lines (not expected inside the heliopause or at Earth). Thus, variations in the nearby galactic cosmic ray flux would be due to specific events or processes that may be transient, depending on the nature of the source.
Found this PDF. Nice read.
https://www.ethz.ch/content/dam/ethz/special-interest/phys/particle-physics/star-n-planet-formation-dam/documents/Courses/Astrophysics%20III%20FS%202018/astro3c4_18.pdf
“It’s probably not sufficient over a long period of time to believe the Sun is the single limiting factor in cosmic ray flux on Earth.”
According to his theory it’s not. He theorizes that cosmic rays increase as the solar system passes through galactic arms as it makes its way through its galactic orbit (if I recall correctly).
Cosmic, indeed, comes from “out there”.
The issue is how it is diminished by the changing magnetic field.
Often clarified as Galactic Cosmic Rays (GCR) to indicate from the galaxy and outside our solar system. See articles on Svensmark Galactic Cosmic Rays
Buckeye Bob
CR means all cosmic rays. GRC means galactic cosmic rays originating outside the solar system. The sun produces lots of CR.
Warren, I caution everyone to beware of Wikipedia for accuracy about anything other than celebrities birth and death dates.
+50
So since the mid 1990’s, the solar wind has weakened, and cloud cover has declined. That’s a great negative feedback.
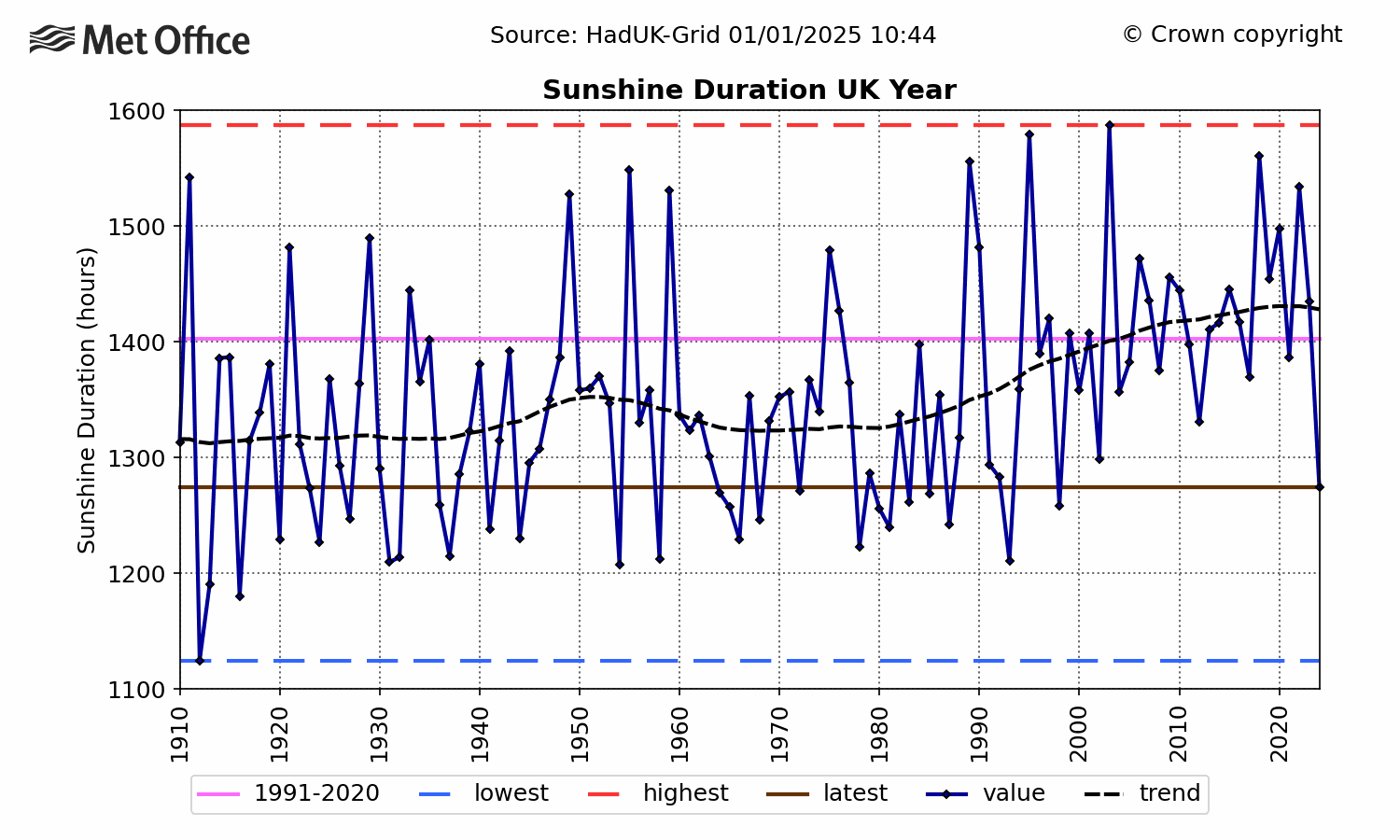
The same variation as we have in Sweden-17% more sun hours in 40 Years.
UK goes from 1240 to 1440 or +16%
Remarkable!
The UK does not the whole world make!
It’s a global signal teleconected to the AMO envelope, including the southern hemisphere.
http://hockeyschtick.blogspot.com/2012/10/new-paper-finds-large-increase-in.html
https://sunshinehours.net/category/sunshine/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364682611002227
“A search has been made for a contribution of the changing cosmic ray intensity to the global warmingobserved in the last century. The cosmic ray intensity shows a strong 11 year cycle due to solar modulation and the overall rate has decreased since 1900. These changes in cosmic ray intensity are compared to those of the mean global surface temperature to attempt to quantify any link between the two. It is shown that, if such a link exists, the changing cosmic ray intensity contributes less than 8% to the increase in the mean global surface temperature observed since 1900.”
“Discussion of the results
The contribution of cosmic rays to the increase in the mean surface temperature of the Earth during the last century has been assessed by comparing the shapes of the variation in the cosmic ray rate to those of the observed mean global surface tempera- tures. The long term variation gives an upper limit on the contribution of cosmic rays to GW of less than 8% of the observed increase in temperature. It is difficult to gauge the statistical confidence level of this value since the change in cosmic ray rate is rather uncertain and depends on the precise start date. The result is conservative since if we had chosen the start date to be 1955 rather than 1952 the change in cosmic ray rate would have been zero giving a limit of 0%.
Full paper….
http://zero.sci-hub.tw/1335/39100e0f1dd730435357db13716ce57d/sloan2011.pdf
I would appreciate a transcript.
Meh. We already know that Milankovitch effects cause the major climatic changes.
You people are morons you are walking past the most important force in the climate change argument. That force is surface tension. Surface tension makes it impossible for water to accept heat through its surface. Get yourself a bucket of water and a heat gun and try putting heat through the surface of the water.
“Get yourself a bucket of water and a heat gun and try putting heat through the surface of the water.”
Warming is not added to the oceans via back-radiated LWIR.
It instead slows cooling of the oceans to space.
Same as on land.
I have a powerful cutting laser, I’m going to try it.
And thus, the main “temperature” role of CO2 in the atmosphere.
CO2 acts like a time- delay circuit, slowing IR radiation to space, by milliseconds, at most.
No, it doesn’t time-delay it. How would that work? It is the measurements at top of atmosphere that confirm the (‘greenhouse’) behavior is as radiative physics predicts. Those measurements would be picking up the ‘time-delayed’ infrared at affected wavelengths, if that was all that is happening.
In North Mediterranean sea surface temperature varies from about +13C in the winter to about +25 in the summer. How come?
Solar SW.
RMB
Science = “Take no one’s word for it”.
Do the experiment and observe the results. e.g. see Boil water using the sun. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IozwteTqPv4
Hmmmn.
Now, let’s see you “boil water using the sun” at 5:30 in the morning … 8<)
RACookPE1978 Please engage brain before opening mouth.
I was responding to RMB’s “Get yourself a bucket of water and a heat gun and try putting heat through the surface of the water” – No time nor sun mentioned.
Leave the bucket out in the sun for a few hours then check whether the top few cms are warmer than the rest of the water
Or try swimming in a still dam, even in the tropics .
The top metre or so will be warm. Below that quite cold.
A bit of a shock to the inexperienced who dive in.
The top metre has been warmed by something….seems the surface tension doesn’t keep all heat out
And in oceans water is thrown into the air in choppy conditions and falls back.
That’s one mechanism for heat transfer, for both warming and cooling depending on respective temperatures
He pointed out the “Solar SW”, or short-wave photons directly impacting and penetrating water will warm it via energy absorption and thermal re-emissions, and where the angle of incidence may not matter much at particular SW frequencies as they don’t reflect much but penetrate until scattered out again, or the E is absorbed into the water.
What he’s saying is the thermal kinetic impacts of the atmosphere’s molecules do not heat the upper layer of water, due to surface tension quashing the kinetic impacts. Photons being absorbed into the water do it (plus particulates and solutes will also alter the rate of absorptions and scatterings of photons, and not just an angle of incidence or cloudiness, etc).
Essentially a straw man argument (imagining mainstream theory claims the atmosphere is warming the ocean via conduction, rather than via radiation).
A thousand watts per square meter of sunlight shines on the ocean surface if the sky is cloudless. A cloud can reflect 800 watts of sunlight before it gets to the surface. Svensmark’s “Cosmic-Rays-make-clouds” hypothesis is marginally interesting but nowhere near as provable as a “degree warmer ocean makes 7% more water vapour which becomes clouds” hypothesis.
Anthony–thanks for publishing this one on this site.
This is the best popularization by Svensmark that I have seen.
Yup, it works in the lab and the guys running the big accelerator in Europe did not want him to run the experiment.
Science prevailed.
It works on “Forbush” variations in the order of days.
And Shaviv has shown correlations out to something like 32 million year periodicity.
With just a BSc in geophysics in 1962 I’ve checked my understanding of this theory with a Prof Emeritus, Geology and a Prof Emeritus in Physics at Princeton.
I don’t find Svensmark hypothesis particularly convincing. While it is clear that solar variability has a great impact on climate in the decadal to millennial timescale, it does not appear to be due to changes in cosmic rays, that on a centennial to millennial timescale show a great dependence on changes in the geomagnetic dipole. Over the Holocene the change in cosmic rays reaching the Earth has been the opposite to what the hypothesis requires, and then we have the problem of the Laschamp event, when 41 kyr ago cosmic rays levels went through the roof due to a geomagnetic short reversal at a time that climatically shows no difference according to every proxy available.
Most hypotheses turn out to be incorrect, and that is particularly true of hypotheses that are not well supported by evidence.