Are we in a solar grand minimum? We’ve seen this before, but now predictions are for an extremely weak solar cycle ahead.
Today is the summer solstice in the northern hemisphere. The sun has been without a single observable sunspot now for over a month – 33 days according to NOAA and SIDC data. Spaceweather.com says:
“This is a sign of Solar Minimum, a phase of the solar cycle that brings extra cosmic rays, long-lasting holes in the sun’s atmosphere, and a possible surplus of noctilucent clouds. “

There’s been sightings of the electric blue noctilucent clouds as far south as Joshua Tree, near Los Angeles, and many many other locations. But one of the most interesting things is due to the fact that the Sun’s magnetic field has weakened, more cosmic rays are now bombarding Earth and some airline flights are seeing doses of radiation up to 73 times that which we’d see at ground level.
For example, a flight from Chicago, IL to Teterboro, NJ which flies at 45,000 feet gets 73.3 times the radiation dosage than a traveler would experience at ground level. A typical commercial flight across the United States gives you about 40x exposure – about the same amount of radiation as a typical dental x-ray. The Chicago-Teterboro flight is almost double that. Frequent air travelers during the solar minimum like we have now would get an even more elevated dose of cosmic rays.
Spaceweather.com is monitoring passenger flights:
We are constantly flying radiation sensors onboard airplanes over the US and and around the world, so far collecting more than 22,000 gps-tagged radiation measurements. Using this unique dataset, we can predict the dosage on any flight over the USA with an error no worse than 15%.
E-RAD lets us do something new: Every day we monitor approximately 1400 flights criss-crossing the 10 busiest routes in the continental USA. Typically, this includes more than 80,000 passengers per day. E-RAD calculates the radiation exposure for every single flight.
The Hot Flights Table is a daily summary of these calculations. It shows the 5 charter flights with the highest dose rates; the 5 commercial flights with the highest dose rates; 5 commercial flights with near-average dose rates; and the 5 commercial flights with the lowest dose rates. Passengers typically experience dose rates that are 20 to 70 times higher than natural radiation at sea level.
Here is a table of recent “hot flights” arranged by radiation dosage level:

There’s now a dedicated website setup for monitoring this https://www.radsonaplane.com/
Meanwhile, the sun seems to be in a deep slumber, PerspectaWeather reports:
The sun continues to be very quiet and it has been without sunspots this year 62% of the time as we approach what is likely to be one of the deepest solar minimums in a long, long time. In fact, all indications are that the upcoming solar minimum may be even quieter than the last one which was the deepest in nearly a century.

In addition, there are now forecasts that the next solar cycle, #25, will be the weakest in more than 200 years. The current solar cycle, #24, has been the weakest with the fewest sunspots since solar cycle 14 peaked in February 1906. Solar cycle 24 continues a recent trend of weakening solar cycles which began with solar cycle 21 that peaked around 1980 and if the latest forecasts are correct, that trend will continue for at least another decade or so.
Full story here
Discover more from Watts Up With That?
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Exposure to ‘cosmic radiation’ (high-energy protons and atomic nuclei) is making airline passengers into Genetically Modified Organisms! Oh noes – GMOs! Oh, the humanity….. /s
I’ve wondered if GCRs and background radionuclide radiation may be the mechanism driving evolution.
They are certainly contributors, Gary!
Mainly the flight crew, they are under the windshield which allows a lot more rays to hit them, in addition they are in the air much more than most passengers.
There is far more mass within the plexiglass layers of the Windshield than within the skin of a jet. Optical transparency will not equate to a lack of attenuation of particles impacting it.
Supposedly, with more cosmic rays we should see more eruptions of volcanoes with silica-rich magmas.
Cosmic rays don’t even penetrate all the way through the atmosphere, much less through miles of rock.
Even if they did, the total energy isn’t enough to make a measurable difference in the temperature of magma.
Muons penetrate deeply into the earth, and they’re either cosmic radiation or generated by cosmic radiation. They don’t heat already hot magma, but apparently cause nucleation of bubbles in supersaturated magma that results in explosive eruptions.
There is a group of solar scientists that argue the sun does not change and that there was no Maunder minimum and the sunspot record should be changed to agree with that position.
The problem with the sun cannot change theoretical position is it unfortunately leads one to ignore current observations that support the assertion that there has been a significant change in the sun.
William: There is observational evidence the Maunder Minimum happened. It is a fact that are cyclic climate changes in the paleo record including very large climate changes, such as the Younger Dryas, that correlate with solar cycle changes and geomagnetic field changes. There is no explanation as to cause of any of the observed climate/geomagnetic field changes.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1507.05191v1
The Maunder minimum (1645–1715) was indeed a Grand minimum: A reassessment of multiple datasets
Aims. Although the time of the Maunder minimum (1645–1715) is widely known as a period of extremely low solar activity, claims are still debated that solar activity during that period might still have been moderate, even higher than the current solar cycle # 24. We have revisited all the existing pieces of evidence and datasets, both direct and indirect, to assess the level of solar activity during the Maunder minimum.
Results. The level of solar activity during the Maunder minimum is reassessed on the basis of all available data sets.
Conclusions. We conclude that solar activity was indeed at an exceptionally low level during the Maunder minimum. Although the exact level is still unclear, it was definitely below that during the Dalton minimum around 1800 and significantly below that of the current solar cycle # 24.
Claims of a moderate-to-high level of solar activity during the Maunder minimum are rejected at a high confidence level.
Is there observational support that something unusual is happening to the sun? Yes!!!
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/440/1/012001/pdf
The peculiar solar cycle 24 – where do we stand?
There were signs from the solar interior too that something unusual was going on inside the Sun. Data on solar oscillation frequencies that can be used to deduce conditions inside the Sun (see e.g. Christensen-Dalsgaard 2002). Solar oscillation frequencies are known to change with solar activity (Woodard & Noyes 1985; Elsworth et al. 1990; Libbrecht & Woodard 1990; and more recently Basu 2002; Howe et al. 1999).
These solar-cycle related changes are also correlated with solar activity indices (Jain & Bhatnagar 2003). The solar cycle-related change in the frequency of a given mode is known to be a function of the frequency of that mode.
High frequency modes have larger shifts than lower-frequency modes. and this implies that solar-cycle related changes in the solar structure occur predominantly in a thin sub-surface layer of the Sun (Nishizawa & Shibahashi 1995). The Birmingham Solar Oscillation Network (BiSON) has been collecting solar oscillation data for over thirty years. Its observations cover cycles 22 and 23 in their entirety and of all cycle 24 to date. The data also cover a few epochs of cycle 21.
Basu et al. (2012) showed that the frequency-dependence of solar-cycle related shifts was different during cycle 23 compared to cycle 22.
The correlation of the different solar activity indices with the frequency shifts was affected, and in particular, they showed that while the International Sunspot Number (ISN) and the 10.7 cm flux was correlated with the change frequencies during cycle 22, this correlation was lost after the maximum of cycle 23 (Figures 2 and 3 of Basu et al. 2012). Had this change in behaviour been detected in a timely fashion, it would have alerted us to the fact that the Sun was going through an unusual phase.
The correlation between frequency change and activity indices was regained for the high-frequency modes (ν > 2400 µHz) in cycle 24, but not for modes with lower frequencies.
The above examples are just some of the unusual characteristics of the minimum that have been documented in the proceedings of the SOHO 23 workshop entitled “Understanding a Peculiar Solar Minimum” (ASPCS Vol, 428). Other noteworthy differences include the fact that the fast solar winds were confined to higher latitudes — using interplanetary scintillation measurements Manoharan (2012) showed that at 125 R…
The peculiar solar cycle 24
SC24 was not particularly peculiar. It was much like SC14, SC12, and SC5.
Instead of looking at sequences of spotless days, I prefer to keep reading info about the long term:
http://www.sidc.be/silso/node/152
Well, that’s the problem with sunspots as a measure of solar activity. Once they drop to zero there is no measurement of solar activity. 10.7 cm solar flux does not go to zero and therefore solar activity can be better gauged. So far the month with lowest 10.7 cm flux was last November. It will be interesting to see what the measurement for June ends up being.
Javier
You were told so many times about the SSN vs. 10.7 correlation that such comments become really ridiculous.
J.-P. D.
Unlike most, instead of trusting what I am told, I actually check the data.
And what the data says is that 10.7 cm adjusted flux is less noisy and not capped at zero, and therefore more useful for defining the solar minimum in real time.
Observe how in August 2009 the number of sunspots was zero, yet the minimum had been nine months before. 10.7 cm adjusted flux however was two units higher in August 2009.
Keep counting sunspots if you want. I keep an eye on 10.7 cm flux because they don’t always give the same information and 10.7 in my opinion can be trusted more.
Now it is your comment that looks ridicule.
Sorry Javier, but…
… you were told of that some months ago by a person who really checks the data. Here is – again – a percentile based comparison of SSN with 10.7:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ShXgzae4Fr_fOs9kWJiSzD8yXkcewQZY/view?usp=sharing
{ The chart ends with Dec 2017 because the F10.7 record provided by LISIRD:
http://lasp.colorado.edu/lisird/data/noaa_radio_flux/
had a big hole in 2018). Maybe you have a better source allowing me to finalise the comparison. }
You see thus how wrong it can be to cherry-pick a single date within a long time series.
*
But how ridiculous you behave you see moreover when having a look at the chart below, showing the monthly differences between SSN and 10.7 for the same period:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1yjvQYk0Q7oMxdpl9x_w3hriiBQiYzvQH/view
How is it possible to discuss the tiny differences around 2009 while ignoring that
– there were much greater ones within several other years, but
– the average difference for 1948-2017 was 0.07 % ?
But this is, like yours, only my simple layman’s look at the stuff.
What scientifically more educated people do, you can grasp when carefully reading the following ducument:
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/85d9/363b9c51d30ec3a1a2db3affcad3936798ad.pdf
The abstract:
Il n’est jamais trop tard pour apprendre.
It seems you answered without reading my comments. I am discussing here that SSN “at the time of solar minima” is not the best way to measure solar activity. And this is because of two problems:
1. It has more noise. And part of it is the way sunspots are counted as a single sunspot counts as 11 (10 for forming a group and one for the sunspot), while two sunspots count as 12. So they might count 23 sunspots when there are only three in two groups.
2. It is capped at zero. Once there are no sunspots if solar activity goes lower there is no way to know.
10.7 cm flux does not have any of those problems and it is a more reliable way of gauging solar activity during solar minima. And I showed the data that proves it:
It has less noise and defines better the minimum in activity. You can ignore it as much as you want. I don’t care.
Javier
Sorry again, but I still can’t agree with what you pretend concerning the SSN accuracy compared with that of F10.7 when looking at your mid 2007 – end 2009 example using monthly averages.
Here is a graph showing the two plots for this period:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/12QdLjNh8BSQ7UIQxsQbxIOHuB17xMcL3/view
There is no reason at all to prefer F10.7 just because SSN drops down to zero at one place.
It becomes even more evident when you switch to a percentile based comparison where both plots reach zero when showing least data values:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1xTsSUrL2ibv-LtAU9NIaOcOuqidovCAB/view
*
But… here, Javier:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JbUKZwfqBXCu49YoJ5sJVzU1gTSpAyo6/view
you are obviously right. This shows SSN vs. F10.7 for 20019, April 1 till May 31.
People who need / wish to observe daily solar activity certainly won’t rely on SSN, as the F10.7 flux info is much more detailed.
Here I can understand what you mean.
I guess global virtue signaling jet setting does have a price after all.
Perhaps a minor point, but no commercial airliners fly at 45,00 feet. The highest airliner service ceiling I’ve seen is 43,000 feet, and virtually none actually fly above 41,000 feet. The vast majority of flights occur between 30,000 and 40,000 feet.
NickSJ
“The highest airliner service ceiling I’ve seen is 43,000 feet, and virtually none actually fly above 41,000 feet. ”
If I may –
“The highest c u r r e n t airliner service ceiling I’ve seen is 43,000 feet, and virtually none actually fly above 41,000 feet. ”
Concorde had a service altitude of about 60,000 feet.
Now, of course, only seen in museums.
Auto
So, it must also increase radiation at ground level. Do we have data for that?
About 2% up on mid May when the SSN count was around 20-25 points
http://cr0.izmiran.ru/scripts/nm64queryD.dll/mosc?PD=1&title=Moscow&dt=0&base=9600&Res=1_hour&y1=2019&y2=2019&m1=4&m2=6&d1=21&d2=21&h1=19&h2=19
Solar Cycle 25 is starting about right now or will be in a few months. I think those predictions it happened some months ago are proving to be off some.
Regarding solar minimum, the best insight is given by the butterfly diagram. It is easy to see when the new butterfly (however fuzzy) starts forming. Unfortunately, I couldn’t find any that is updated regularly. This one here (Hathaway) was last updated on 02/2019:
http://solarcyclescience.com/bin/bfly.jpg
I found another one here, seems to be updated on 06/2019:
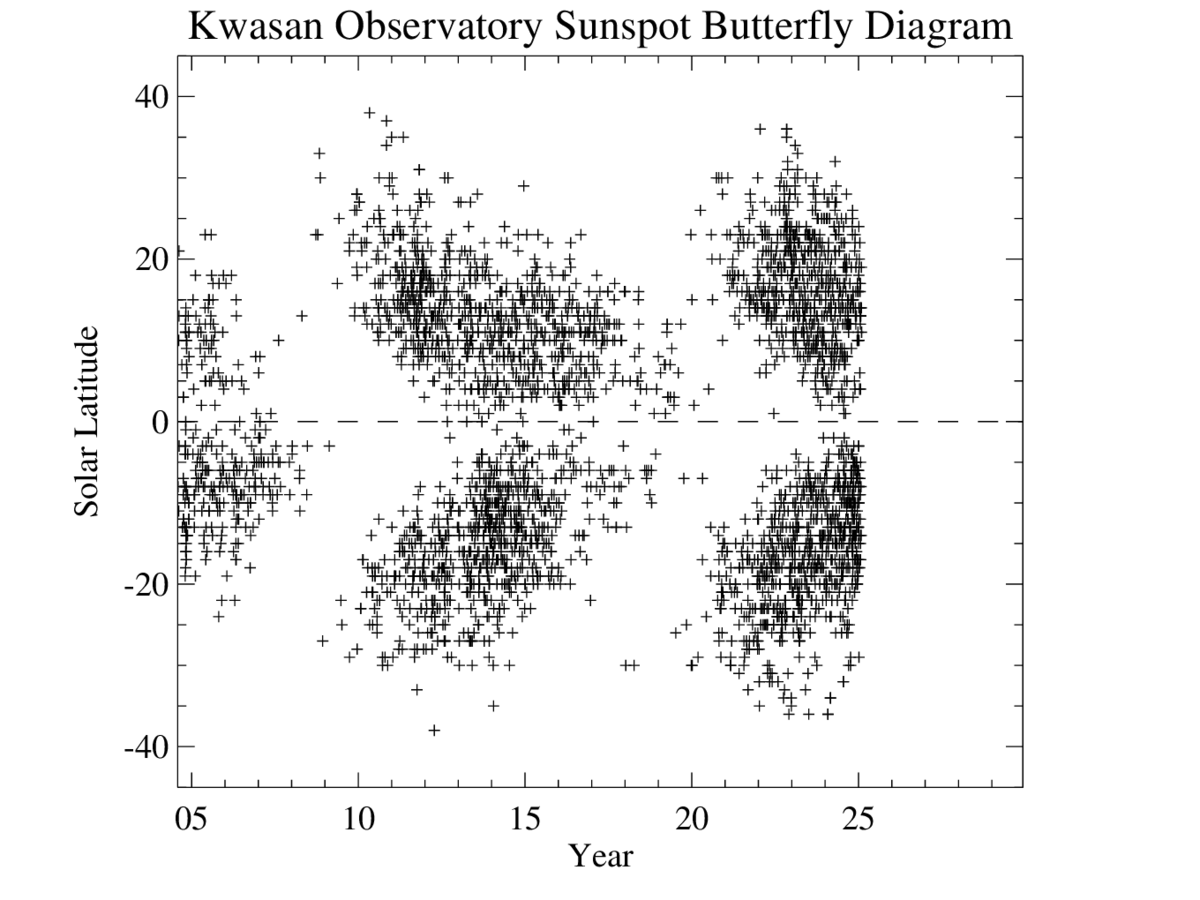
So, there is still NO sign from the sc25 butterfly. That means that the 24/25 minimum is not here yet, and it will be extended and deep, something like the 23/24 one.
Incidentally this would give a few years warning of a “Maunder Minimum”. During the MM the “butterfly” did not extend beyond 20 degrees latitude, and perhaps as little as 15 degrees during the weakest part.
Yes. Sitting on the toilet I often have that a big wind can cause a butterfly!
If Solar Cycle 25 ends up weaker than 24 then Zharkova may end up being right about Cycle 26 literally being dead like in a mini ice-age.
Looking like the lady is correct. I’m buying new skis!
Interesting that Prof. Valentina Zharkova hasn’t been heard from since last October (at least DDG can’t find anything). I wonder what her current thinking is?
I agree. SC 25 should tell us a lot about her predictions if they haven’t changed.
I have heard her paper is going through final stages and should be release shortly. I expect more chatter over her work in the coming months.
Are we in a grand solar minimum? No, not yet anyway.
The Maunder Minimum is considered the last GSM. Since then the Dalton Minimum and Centential Minimum are the next lowest solar activity periods lasting at least two solar cycles.
The Maunder had a group sunspot number of 1.0, while the Dalton averaged 2.3, the Centential average was 3.5, and through 2015 it was 3.7 for solar cycle 24. Using GN = 0.0468*v2SN + 0.6797, solar cycle 24 GN through May 2019 is about 3.1.
Therefore at over three times the GN as the Maunder, we will not reach a low GSM level in SC24.
Solar indices indicate SC24 activity is still so far higher overall than during the last minimum.
Zero sunspots total count at 433 days as of yesterday for this SC24 minimum compared to 817 total for the last minimum.
Too many eager beavers are fear-mongering over a thus-far non-existent GSM. Don’t even talk to me about a GSM until we’ve had a Dalton-like year of zero sunspots first, or five years without reaching 100 sunspots in SC25.
Bob Weber
Thanks, here you show appreciated matter.
It’s easier for them to hype this because there is no detailed accepted scientific definition of a Grand Solar Minimum.
BTW though the author of the article talks about a new method of solar forecasting that is predicting SC-25 to be less active than SC-24, SILSO has not changed it’s projection and still shows SC-25 to have about the same level of activity as SC-24.
“This prediction is now given in the scale of sunspot number Version 2. Therefore, solar cycle 25 will be similar to cycle 24, which peaked at 116 in April 2014.”
http://sidc.oma.be/silso/
Exactly.
“Solar experts predict the Sun’s activity in Solar Cycle 25 to be below average, similar to Solar Cycle 24”
https://www.weather.gov/news/190504-sun-activity-in-solar-cycle
There you read:
“We expect Solar Cycle 25 will be very similar to Cycle 24: another fairly weak cycle, preceded by a long, deep minimum,” said panel co-chair Lisa Upton, Ph.D., solar physicist with Space Systems Research Corp. “The expectation that Cycle 25 will be comparable in size to Cycle 24 means that the steady decline in solar cycle amplitude, seen from cycles 21-24, has come to an end and that there is no indication that we are currently approaching a Maunder-type minimum in solar activity.”
Alarmism in whichever direction is bare nonsense.
Rgds
J.-P. D.
I agree with you on the claim being over hyped. No one knows what level of cooling this trend will peak at. There is one example though of a major temp drop in the NH occurring right in the middle of the Medieval WP. It takes place around 1130 AD, and the drop in temps is the deepest drop on the 2,000 years represented on the graph. … http://www.uni-mainz.de/eng/bilder_presse/09_geo_tree_ring_northern_europe_climate.jpg
Note that around 10 years prior was the initial start of a cool trend. Hekla volcano in Iceland started a violent eruption in 1104 with 30 eruptions in the years which followed. Perhaps Hekla’s eruptions led into a natural cooling trend such as a Gleissberg/grand minimum, and that is why the cooling seen at that point in time was so deep. It lasts about 60 years, which was also the length of the Maunder GM. So imo it would take a major eruption, ie: Iceland, Alaska, Kamchatka all have volcanoes capable of affecting the entire NH.
goldminor
Thanks for your convenient reply focusing on the center of an endless debate about what caused the successive cooling phases between 1000 AD and present.
But… just a question: if you think that Hekla’s 1140 AD eruption with a VEI 4 (and its followers) had such a cooling effect on climate: what then do you think of the effect of all these eruptions noted below, having all occured before the last Maunder GSM?
– 1257 Samalas, Indonesia, VEI 7
– 1280 Quilotoa, Andes VEI 6
– 1452 Kuwae, Vanuatu, VEI 6+
– 1477 Bárðarbunga, Island, VEI 6
– 1563 Agua de Pau, Acores, VEI 5
– 1580 Billy Mitchell, Solomon Island, VEI 6
– 1586 Kelut Island, VEI 5
– 1600 Huaynaputina, Peru, VEI 6
– 1641 Mount Melibengoy, Phillipines VEI 6
– 1650 Kolumbo, Greece, VEI 6
– 1660 Long Island, Papua New Guinea, VEI 6
Please take into account that eruptions with a VEI equal or superior to 5 mostly are able to bypass the Equator. The Samalas eruption in 1257 is known to have caused 15000 deaths in London (33% of its population at that time) during the year 1258.
Maybe you had a look at e.g.
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2011GL050168
I think that every eruption which you listed above can be sen clearly on the JG/U @K tree ring study. That is what I think.
1257 = substantial cold trend, lasts around 60 years
1280 = temps had warmed from prior cold then suddenly plunge cold for another 8 years approximately
1452 = 2nd deepest drop, then warms over 20+ year till around 1477 when temps plunge again for around 6 more years
1563 1580 1586 1600 = a GM at 1560 for 30 years and 80 86 are end of cold trend. 1600 is a temp drop short tern about 12 to 15 years
1641 1650 1660 + all show up as temp drops on the JG/U graph
… http://www.uni-mainz.de/eng/bilder_presse/09_geo_tree_ring_northern_europe_climate.jpg
Yes indeed, I agree.
The interesting point in the JGU graph is imho the running mean showing as usual much more than does a linear estimate alone.
The second point is that during the Maunder Minimum, the running mean’s deviations below the linear trend are minimal in comparison with those around 1150, 1450 etc.
This graph is so interesting that I’ll try to obtain the data source from JGU.
Meanwhile, a passel of climate “scientists” are gathering to apply for a Government grant and author a paper on how mankind’s CO2 emissions over the last 200 years have affected the sunspot cycle.
Rumor has it that the basis for this claim is Earth’s increased radiation forcing of the Sun’s photosphere and coronal environmental energy budgets, estimated at 1.473 x 10^(-18) watts/m^2 per deg-F increase in Earth TOA effective radiation temperature (sunlit side, of course). Oh, lest I forget, that’s with a 2-sigma error band of 2.951 %.
Source?
It is certainly sarcasm. Right?
If sarcasm was a synonym for ignorance, then: yes.
David
he is a jolly joker.
there is no man made warming
anyone believing that the 50-100 ppm CO2 that was added to the atmosphere in the past 50-100 years can do anything on earth or on sun has absolutely no idea of how life came to be what it is now.
About 2% up on mid May when the SSN count was around 20-25 points
http://cr0.izmiran.ru/scripts/nm64queryD.dll/mosc?PD=1&title=Moscow&dt=0&base=9600&Res=1_hour&y1=2019&y2=2019&m1=4&m2=6&d1=21&d2=21&h1=19&h2=19
which was due to a coronal mas ejection i.e a Forbush dip.
The current debate reminded me of some thoughts I had several years ago. I was trying to find a plausible link between solar activity and climate. I reasoned that apart from TSI, the sun interacted with the earth via particle emissions (solar wind), its massive magnetic field and indirectly through modulation of GCRs. I further reasoned that the most powerful mechanism for climate interaction would be via albedo changes. I set about to find a suitable candidate.
Cosmic dust, asteroid fragments and meteor debris enter our atmosphere all the time. Estimates of the amount vary from about 36 thousand tons to 5 million tons per annum. The range 37000 to 78000 tons is often quoted. The huge range suggests that we don’t really know.
NOAA has reported that aerosols in the stratosphere have almost doubled during the decade starting in the year 2000, this at a time when it was thought that terrestrial emissions were constant. The increase had a significant cooling effect that offset some of the warming expected from increased carbon dioxide over the same period. A study reported in the Journal of Geophysical Research (1) claims an inverse relationship between meteor rates and solar activity as measured by sunspot numbers. This fascinating possibility suggests a connection between cooling caused by meteor dust and the solar cycle.
Meteor “smoke” nucleates ice crystal formation in the mesosphere, creating noctilucent clouds (2). Nasa claims that these clouds are known to peak at solar minima. This ties in with the modulation of dust flux by the solar cycle. Some climate scientists regard such clouds as indicators of climate change (3) and suggest that the water is produced by photocatalytic oxidation of the greenhouse gas, methane. Perhaps a simpler explanation is that meteors entering the mesosphere frequently bring their own water in the form of ice.
There is speculation that the metallic dust may interfere with stratospheric chemistry and ozone. It is well established that iron rich dust entering the upper oceans will fertilize phytoplankton (4) growth thus removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and the warming it would otherwise have caused.
So there we have several mechanisms. Meteor dust particles can reflect solar radiation directly by scattering, help to seed clouds, remove CO2 via phytoplankton growth and modify our atmospheric chemistry. The dust entering our atmosphere is greatest when there is low solar activity.
Perhaps there is more to meteor storms than meets the eye.
(1)https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/JA082i010p01455#references-section
(2) https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/aim/news/early-nlcs-2013.html
(3) https://projectpossum.org/research/noctilucent-cloud/about-noctilucent-clouds/
(4) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16370118
You seem to be saying that the location of meteorite ‘dust’ concentration varies with respect to the orbital geometry of earth (which of course varies) during solar activity level changes. And yet the location and intensity of meteorite showers is fairly predictable as we pass through them. So what evidence is there to the contrary?
Personally I find it amazing that Milankovich Cycles explain so much of the features of the palaeo T record but then seems to fail to explain major cyclicity change within the Quaternary record. Which makes me think the sun can undergo signicicant changes over >2my periods that we don’t know about yet, and that the explanation of climate change is not just about geo-tectonic configurations or resulting variable orbital/rotation wobbles. And if there are varying cyclic T periodicity changes recorded that Milankovich Cycles can’t explain, and there are, then it’s conceivable smaller periodic excursions of such a mechanism can occur as well.
Your first reference is from 1977, at the early years of satellite observations. It is really touching that you would embrace a hypothesis that has not found support in 40 years of improved observations. If the author is still alive he would be thrilled to know he got a supporter, unless of course he abandoned his own hypothesis some time later. After all he claimed an inverse relationship between meteors and solar activity after only 8 years of observation, when for a cycle of 11 years, a minimum of 22 years of data would be desirable. By now we must have about 50 years of data, and it is curious that nobody has noticed the same relationship.
+10 …interesting idea, so maybe the metallic dust is an integral part of that layer of the atmosphere, and the change in concentration of the dust is part of what drives shifts in the climate from warm and cool trends.
Is the Earth’s general albedo up? Sources, please.
The current figures below show the NAIRAS prediction of the radiation exposure quantity related to biological risk – Effective dose rate (uSv/hr) – at several altitudes and flight paths. To put the exposure rates into perspective, one chest X-ray is about 100 uSv, and a CT scan is about 8,000 uSv.
http://sol.spacenvironment.net/nairas/Dose_Rates.html
Actually it is unproven that such low dose rates have any biological effect whatsoever. It may even decrease cancer risk.
Possibly but I know of two pilots who died of cancer right after retirement at 65. Of course it could be coincidence.
Pilots are concerned.
Pilots in the UK have been monitored for 40 years. No evidence of any increase in cancer vs control groups.
The important thing is that the Earth’s magnetic field concentrates galactic radiation in specific regions at high latitudes.
http://sol.spacenvironment.net/raps_ops/current_files/Cutoff.html
Just checked: I’m not glowing in the dark.
Therefore no evidence to justify a “radiation worker” pay-rise. Sarcasms set aside, reality is that no one I know in the trade shows concerns for in-flight radiation. Nor has called sick due to radiation overdose.
Does anybody know if this changes the balance between UV-A and UV-B at the earth’s surface?
If this does result in significant cooling whilst CO2 continues to rise, the climate spin doctors will go into overdrive.
“Surface temperatures and sea level have risen to their lowest levels in decades. Polar ice has melted so fast that it has increased exponentially. The climate has degraded into unpredictable instability, and this is precisely what we warned you would happen”
And the gullible masses will swallow it whole.
I have always been under the impression that a lack of sunspots indicated a lower level of radiation, not higher?
True, lower solar radiation which means less solar wind, which means more cosmic rays, when they hit the upper atmosphere cause a lot of secondary radiation. So lower solar radiation=more radiation from cosmic rays.
The sun doesn’t generate the magnetic field that protects the earth from cosmic rays. The earth generates that magnetic field.
So if the radiation at altitude is increasing, then why are the Greens not
telling u to stop flying. After all think of the vast amounts of CO2 being
produced by the jet engines.
But wait, if we ban planes, then how can we continue to go to all of the
big talk fests about climate change, silly thought.
MJE VK5ELL